Lecture Notes 08: DFA-NFA equivalence and RE-FA equivalence
Outline
- DFAs Vs NFAs
- REs Vs FAs
A Slideshow:
GUIDED NOTES (Optional)
DFA-NFA equivalence
Last lecture we asked the question: Are NFAs stronger than DFAs?
Let’s make a claim:
NFAs and DFAs are equally powerful!

The proof approach is by construction (in two steps):
What we know: \(M_{NFA}=(Q,\Sigma,\delta, q_0, F)\)
- Need to construct: \(M_{DFA}=(Q^\prime,\Sigma,\delta^\prime, q_0^\prime, F^\prime)\) that recognizes L(M)
- Prove that \( L(M_{DFA}) = L(M_{NFA}) \)
Step 1: Building the equivalent \(M_{DFA}\)
We need to make the 5-tuple for the DFA equivalent to out NFA:
From NFA to DFA: the states \(Q \rightarrow Q^\prime \)
It’s possible that in an NFA, we could be in multiple states at each step. If we want to emulate the NFA’s behavior, we’ll have to have a state for each combination.
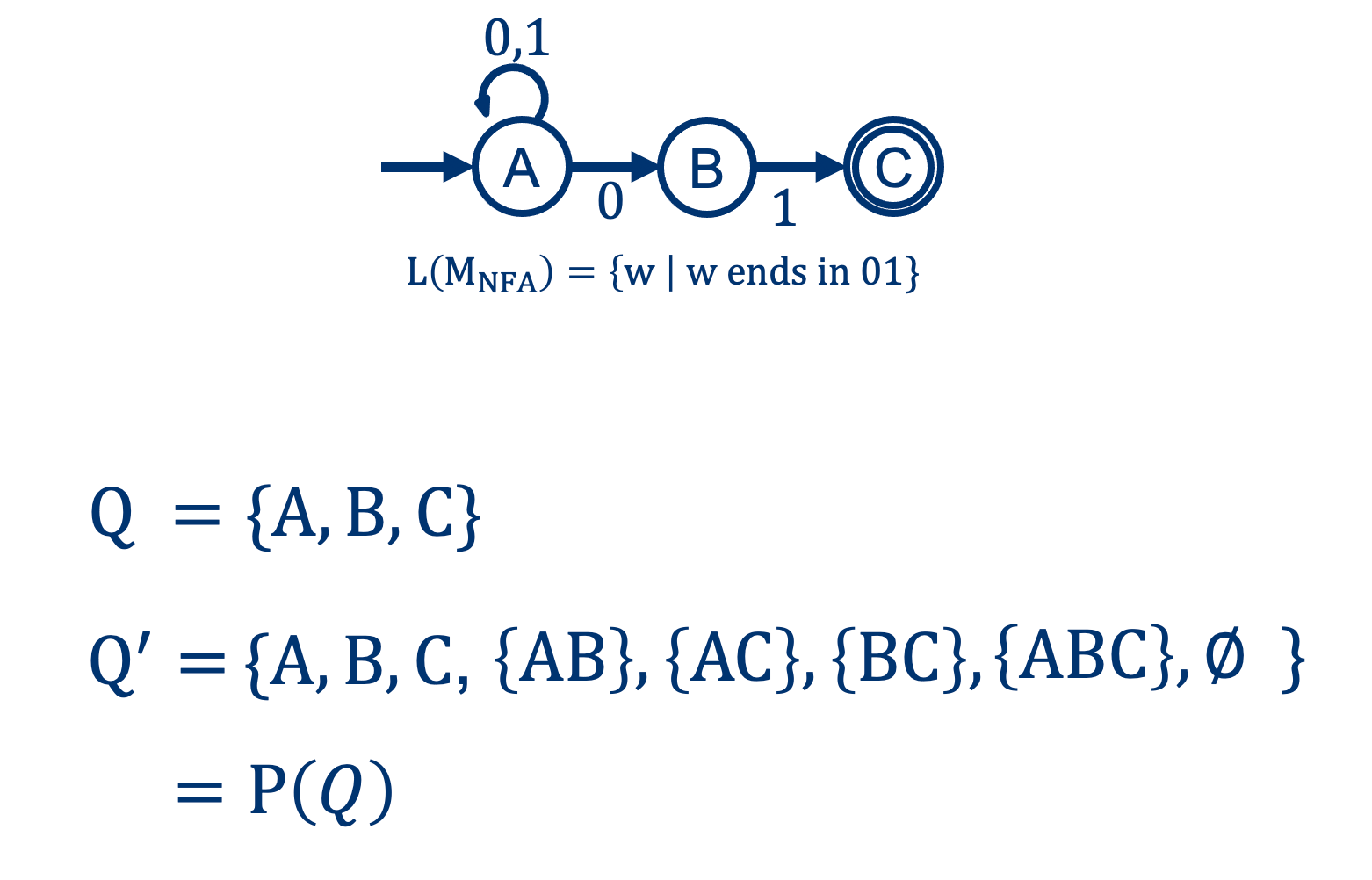
From NFA to DFA: the Start states \(q_0 \rightarrow q_0^\prime\)
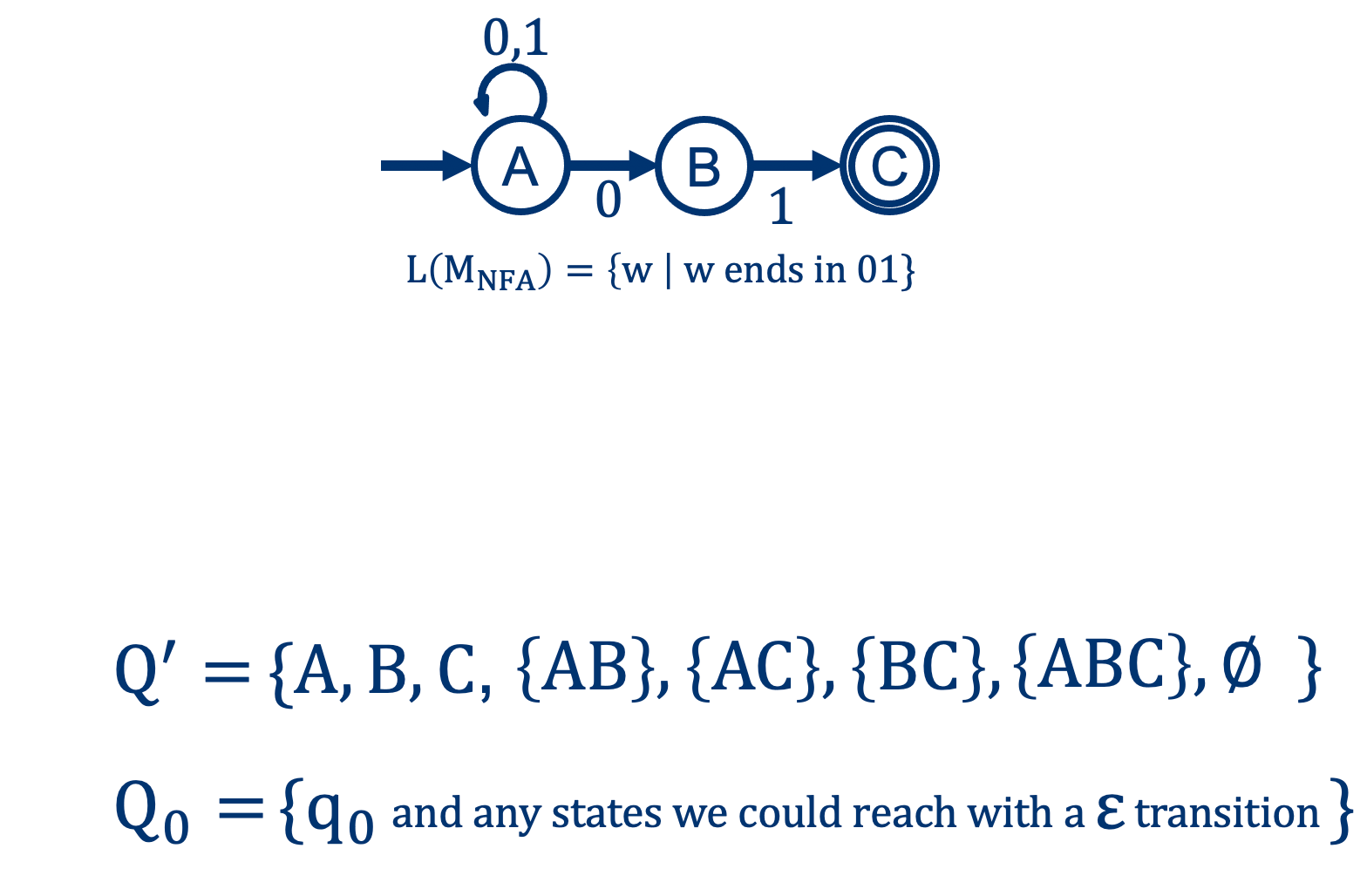
(In this case, only \(A\))
From NFA to DFA: the Accepting states \(F \rightarrow F^\prime\)
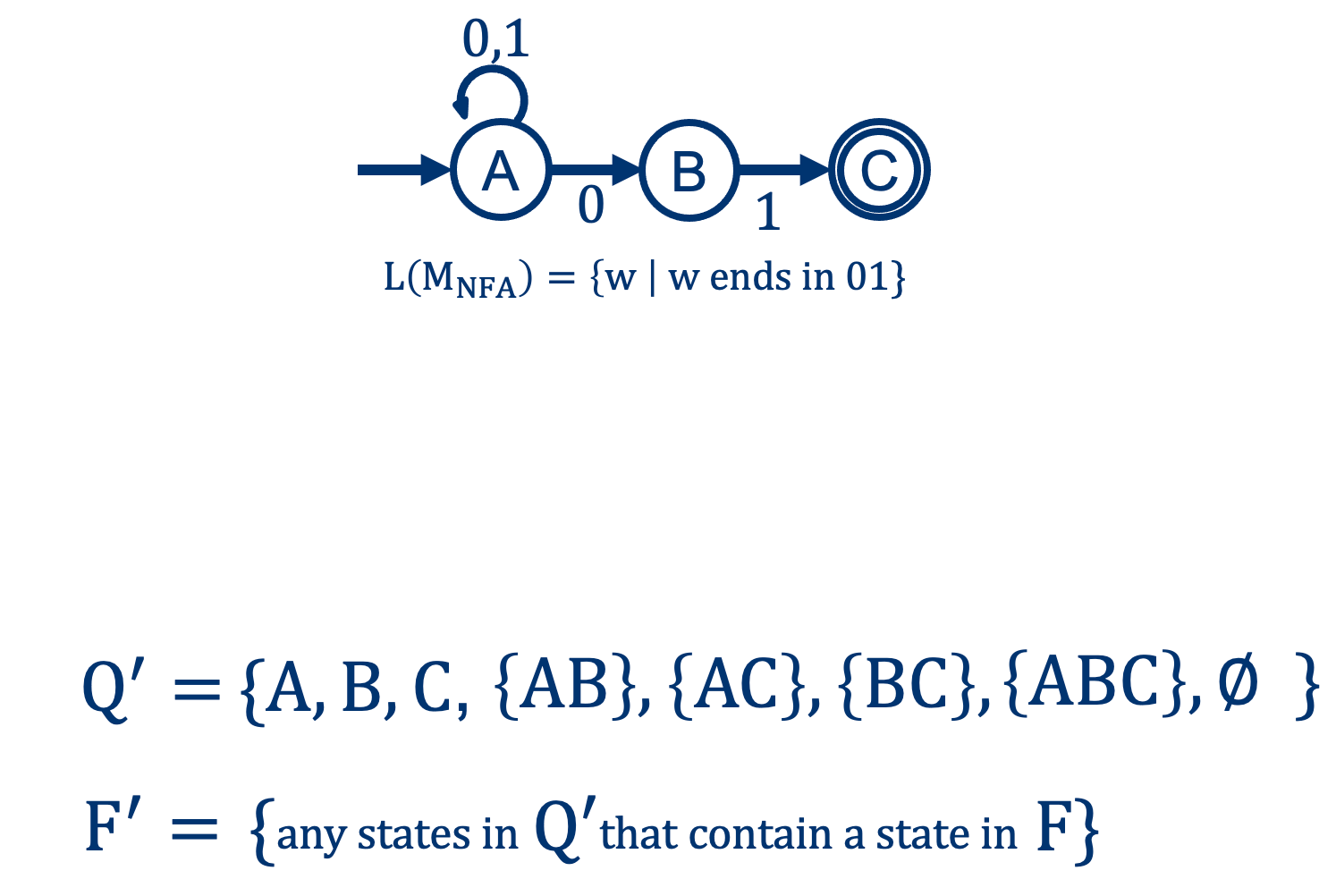
(In this case, \( \{ C, AC, BC, ABC \} \))
From NFA to DFA: the Transitions \(\delta \rightarrow \delta^\prime\)
At each symbol reading, if there are multiple paths to follow, we want to jump the the single state (in the DFA) that is the Union of all the possible destination states (in the NFA) for that symbol.
This can be expressed like this: \[ \begin{alignat}{2} &\delta^\prime ( q, \mathit{a} ) = \bigcup\limits_{p\in q} \delta(\mathit{p}, a) \\ &\qquad \text{ where $q \in Q^\prime$; $a \in \Sigma$} \\ &\qquad \text{ and $q$ can be a set of states from $Q$} \end{alignat} \]
Let’s see it in action.
Example: building the DFA for this NFA
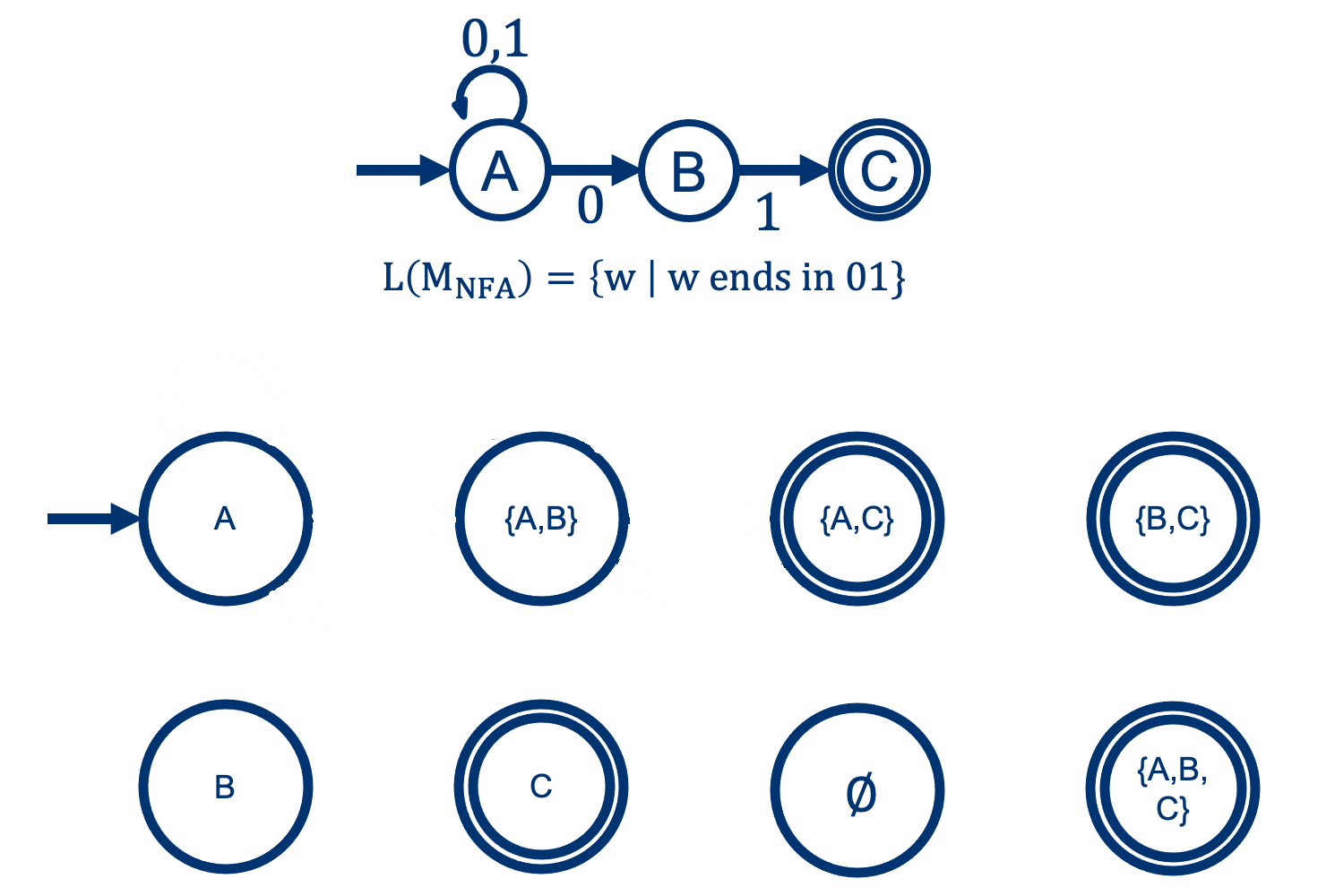
Solution:
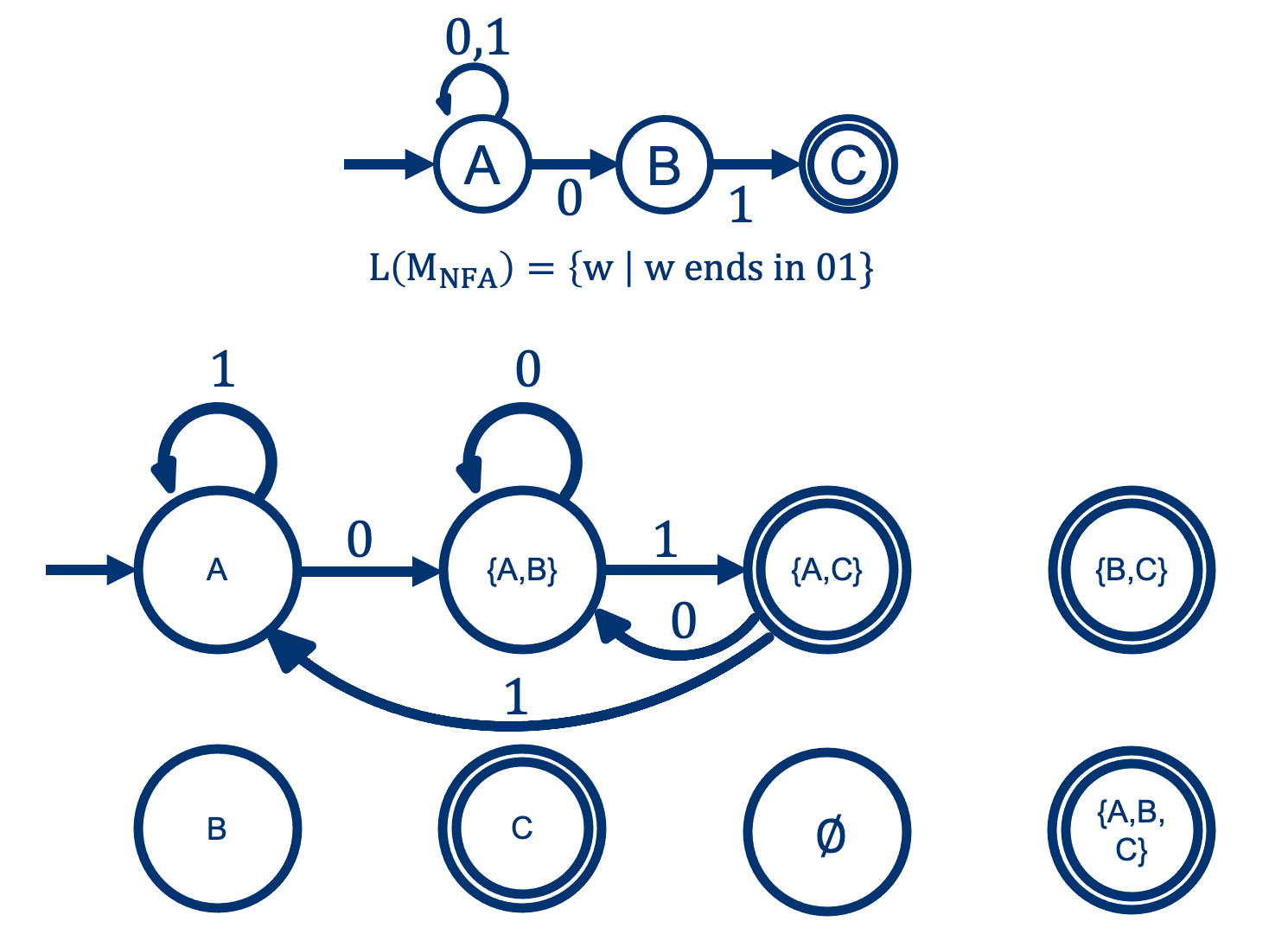
Step2: Prove \(L(M_{DFA}) = L(M_{NFA}) \):

Hint:
To prove that L(DFA) = L(NFA), use induction to show that the result of running the DFA on a word \(w\) (denoted \( \hat{\delta}^\prime(q_0^{\prime} , w))\) is equivalent to the result of running the NFA on the same word [denoted \(\hat{\delta}(q_0, w)\)] for every word $w \in \Sigma^*$.
A summary of recommended steps is:
- Base Case: Prove that \( \hat{\delta}^\prime(q_0^{\prime} , w)) = \hat{\delta}(q_0, w)\) for the base case of \(w = \epsilon\), which is when \( \vert w \vert = 0 \)
- Induction Hypothesis: Asume that \( \hat{\delta}^\prime(q_0^{\prime} , w)) = \hat{\delta}(q_0, w)\) for when \( \vert w \vert = k \)
- Induction Step: Prove that, for a word \(z\) that has a length \( \vert z \vert = k+1 \), (or which we can represent as a concatenation of a word \(w\) of size \(k\) and one more symbol \(a\)), that \( \hat{\delta}^\prime(q_0^{\prime} , z)) = \hat{\delta}(q_0, z)\)
Full proof here:
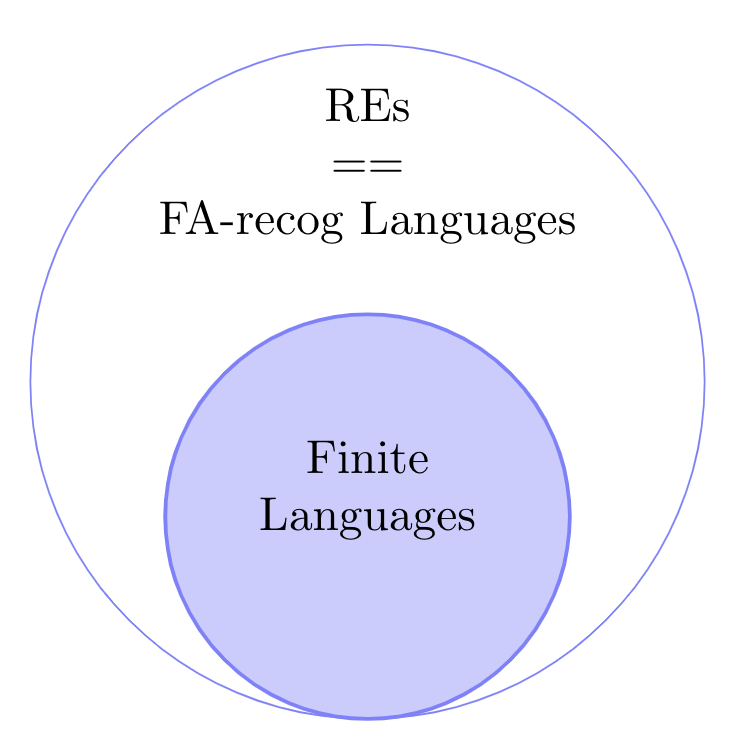
FAs Vs REs
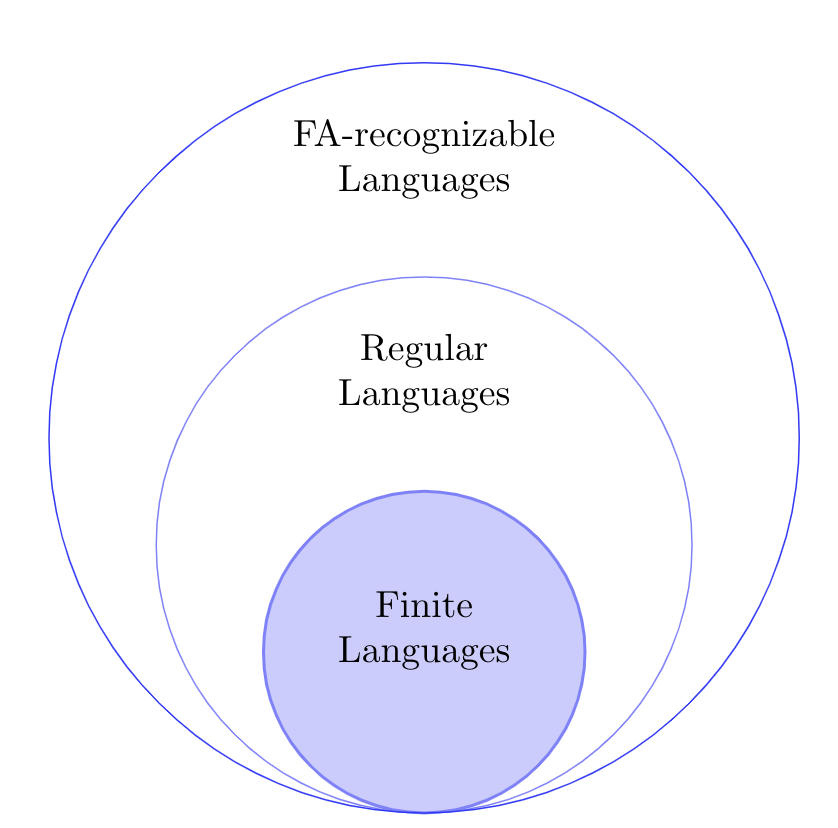
Where do FA-Recognizable Languages stand with respect to Regular Languages?
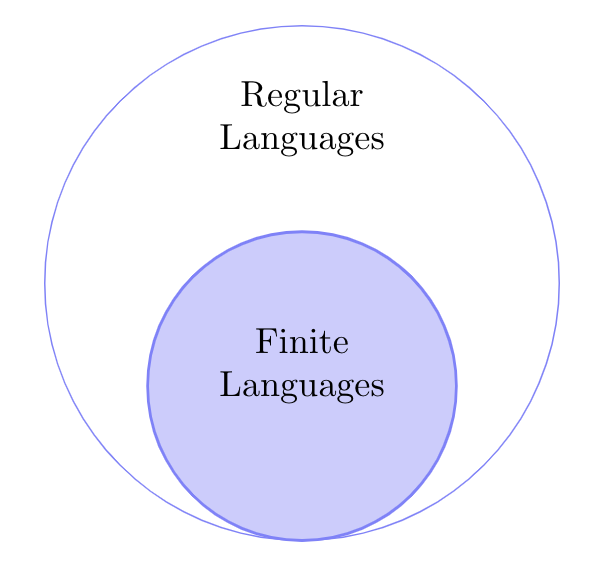
Where are FA-recognizable languageswith respect to Regular Languages?
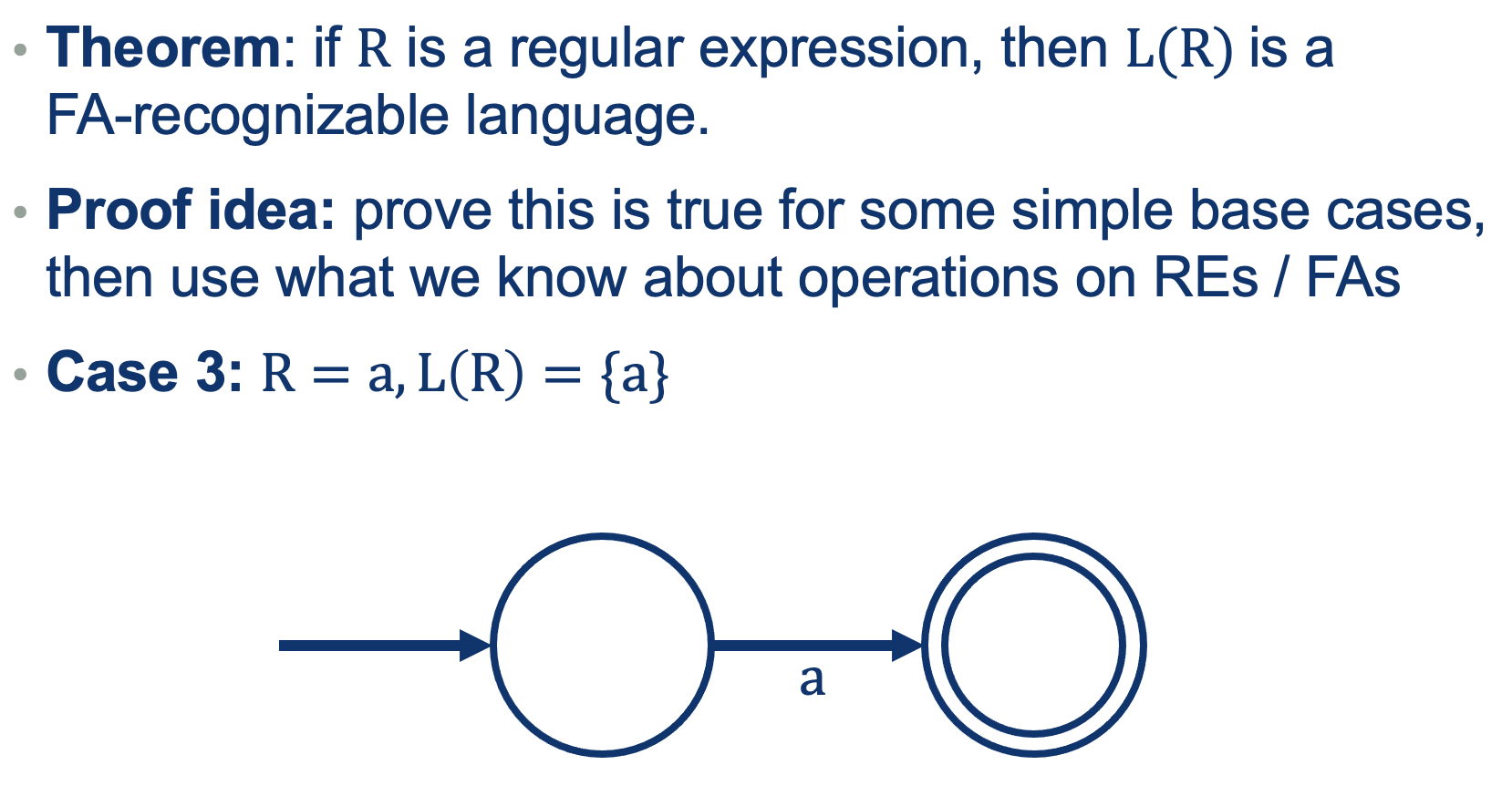
Try Proving: FAs are at least as powerful as REs
We can use the same approach as we did when defining REs (a recursive definition out of base cases).


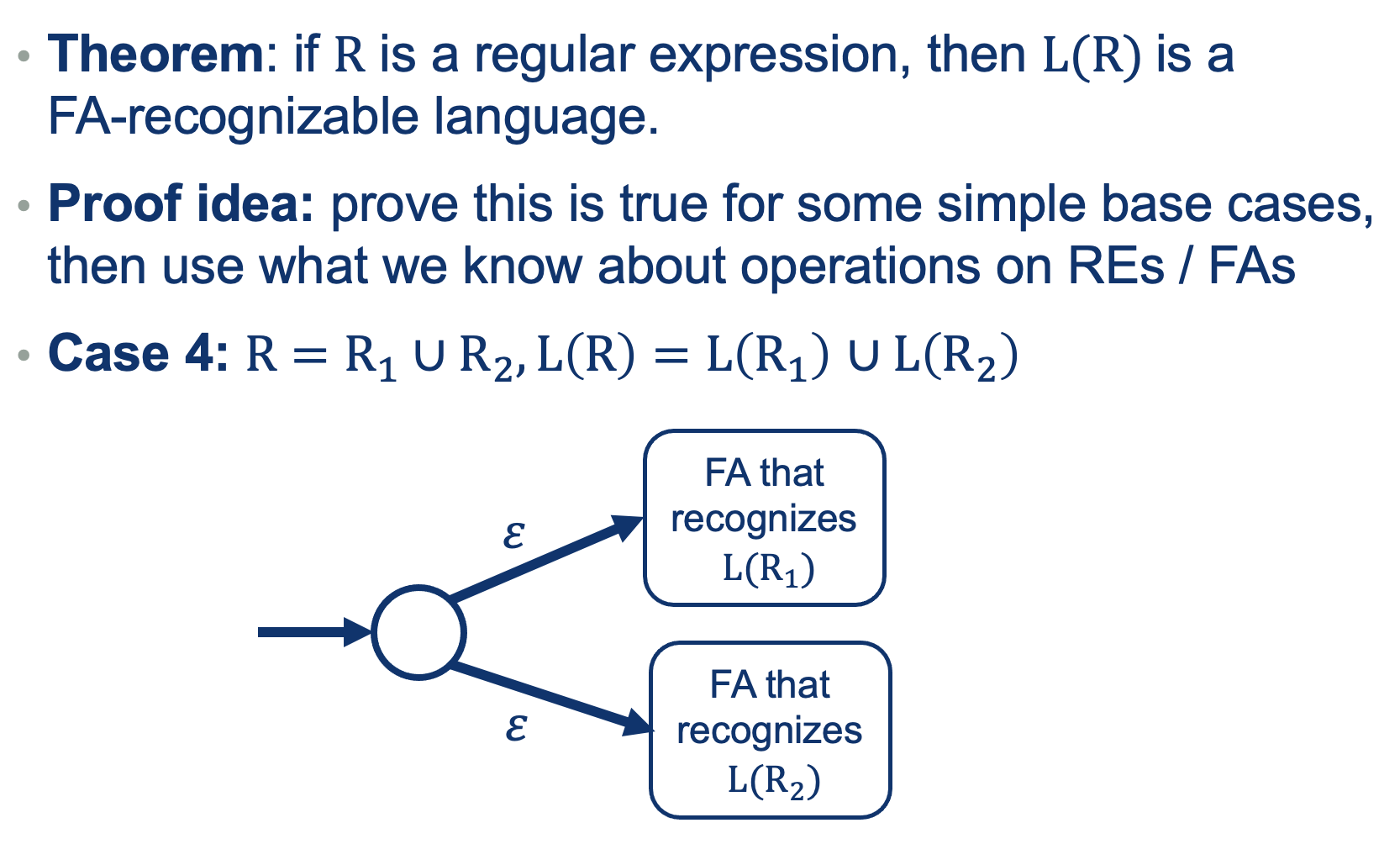
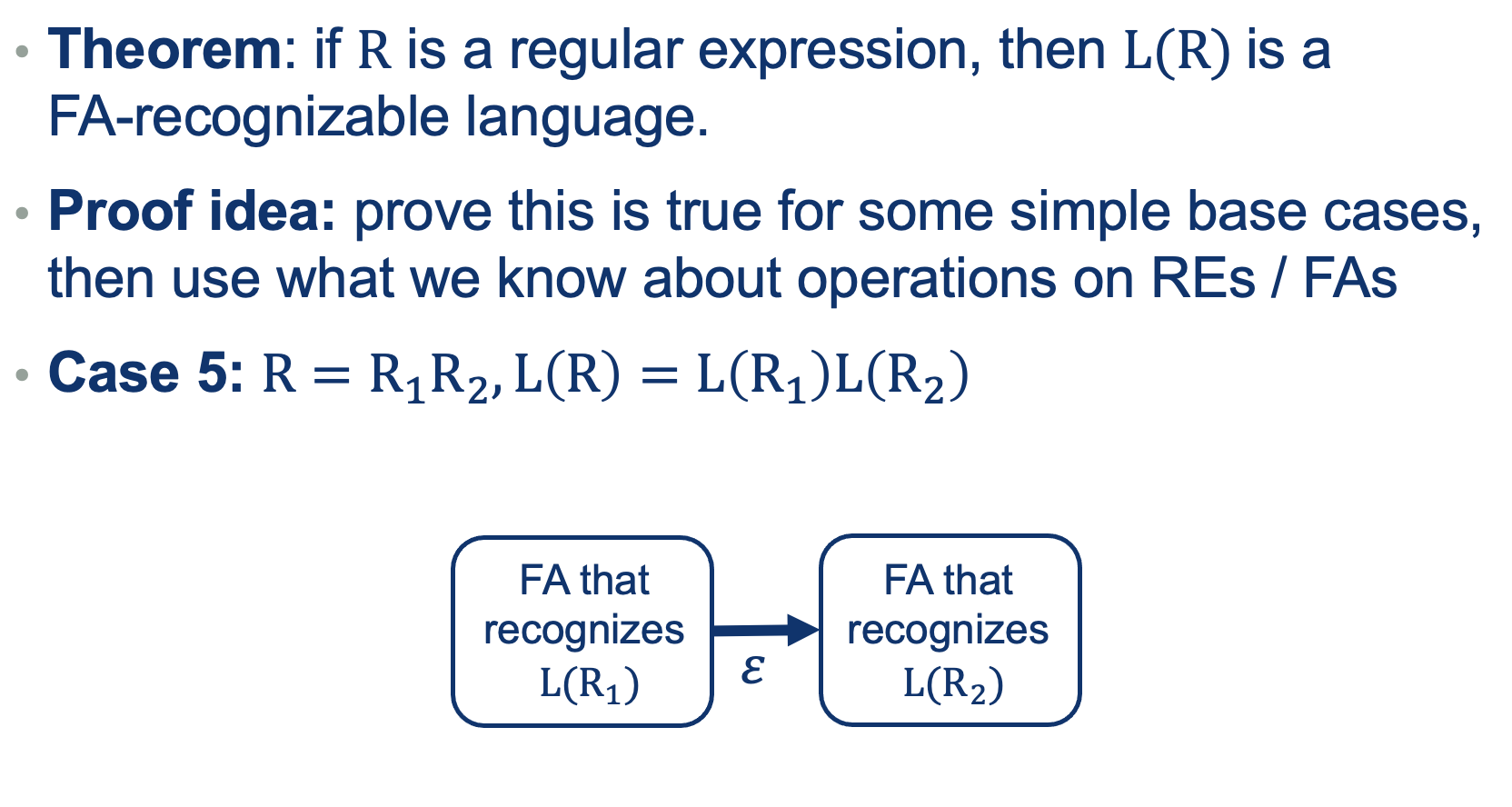
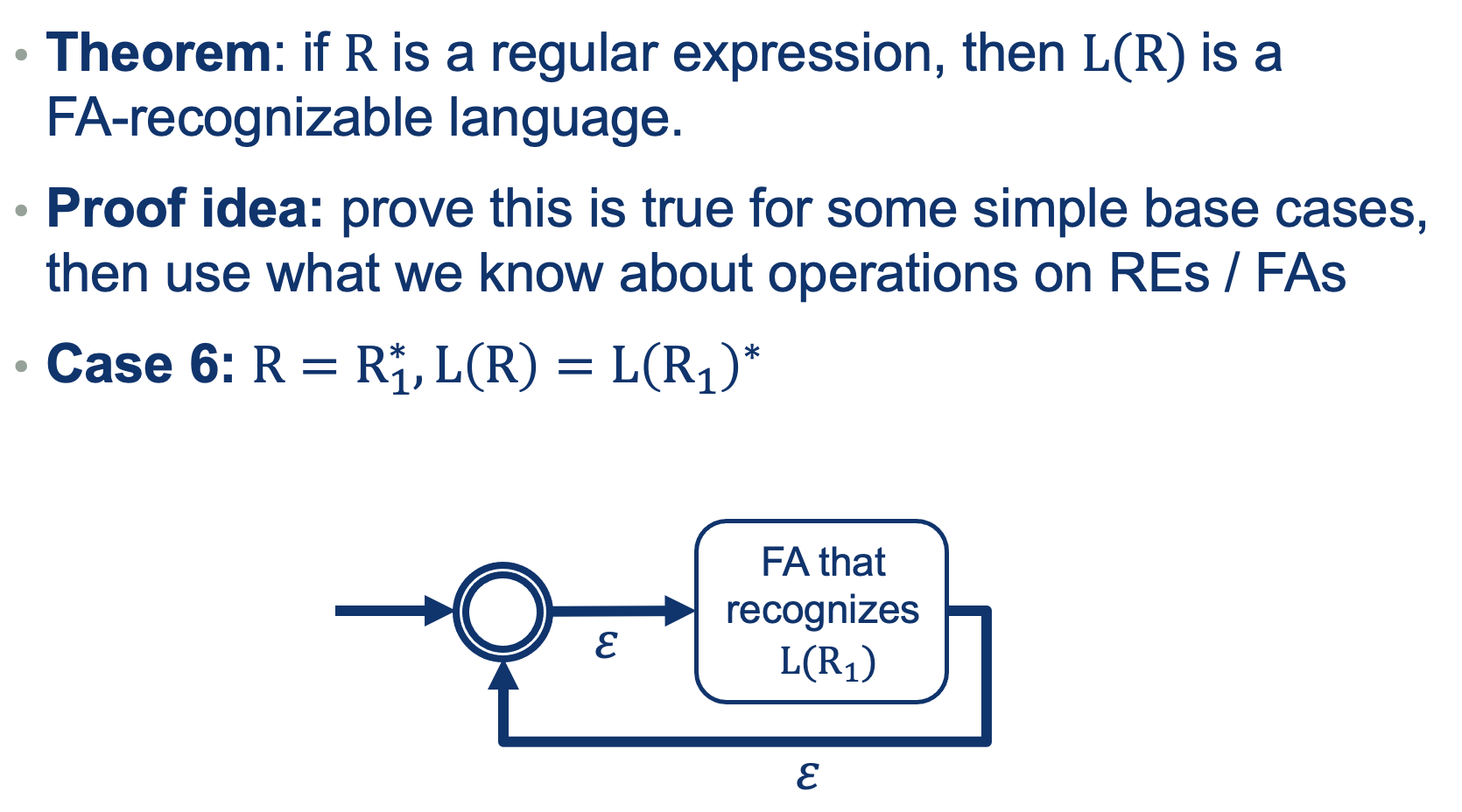
So What did we prove?
NOW, Try Proving: REs are at least as powerful as FAs
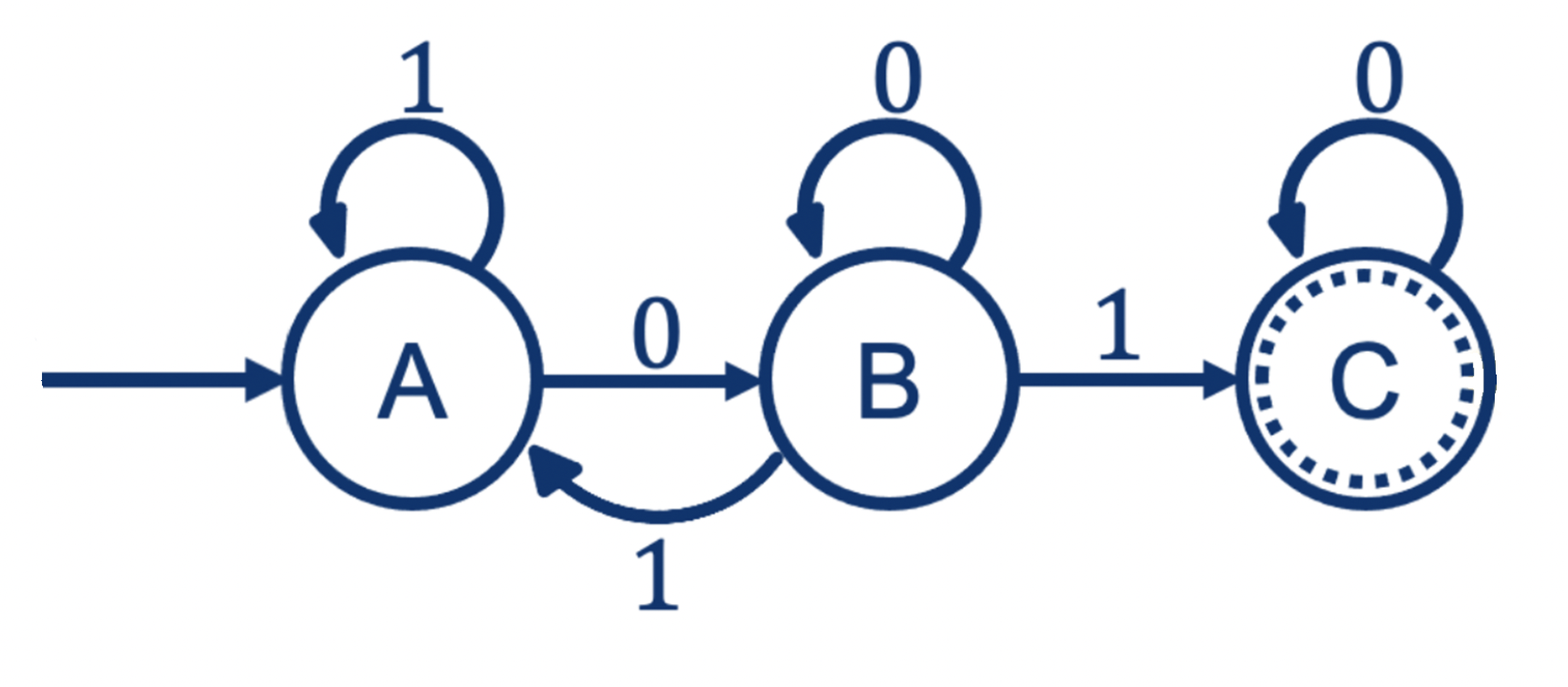
Example FA:
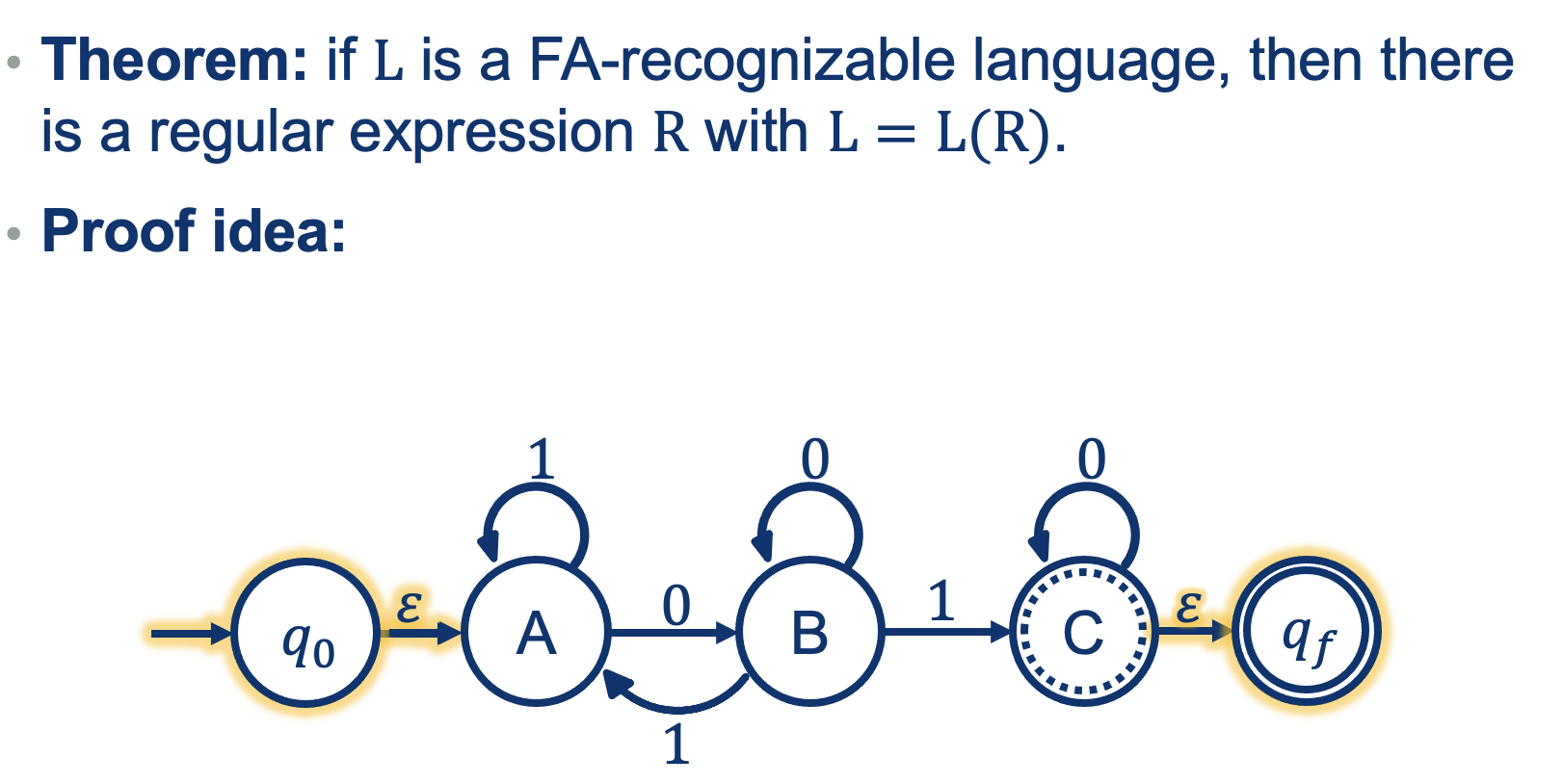
Proof Idea:
convert the FA that recognizes L into a RE
Step 1: modify the FA so that
- the start state doesn’t consume any letters
- there is only one final state
- the final state doesn’t consume any letters
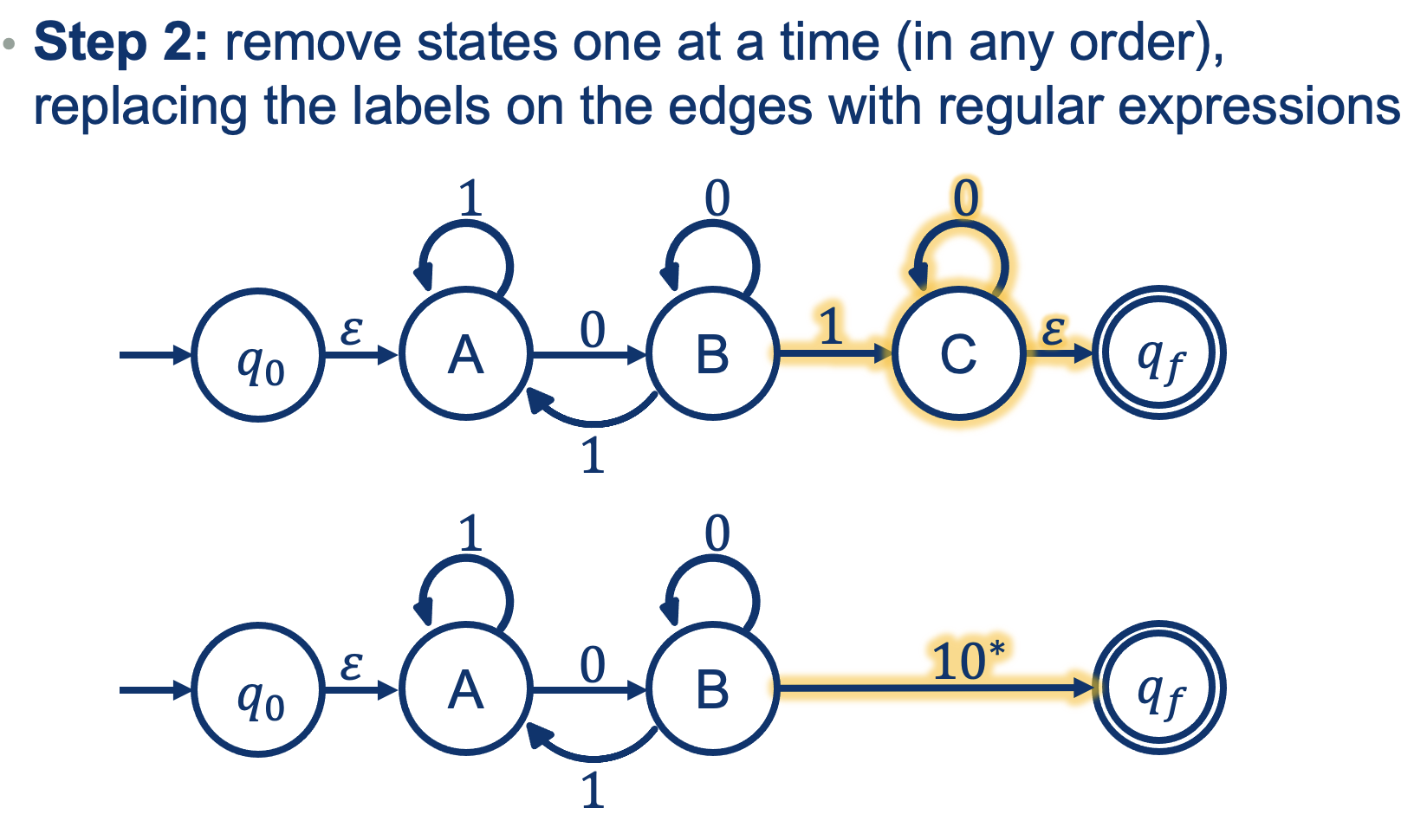
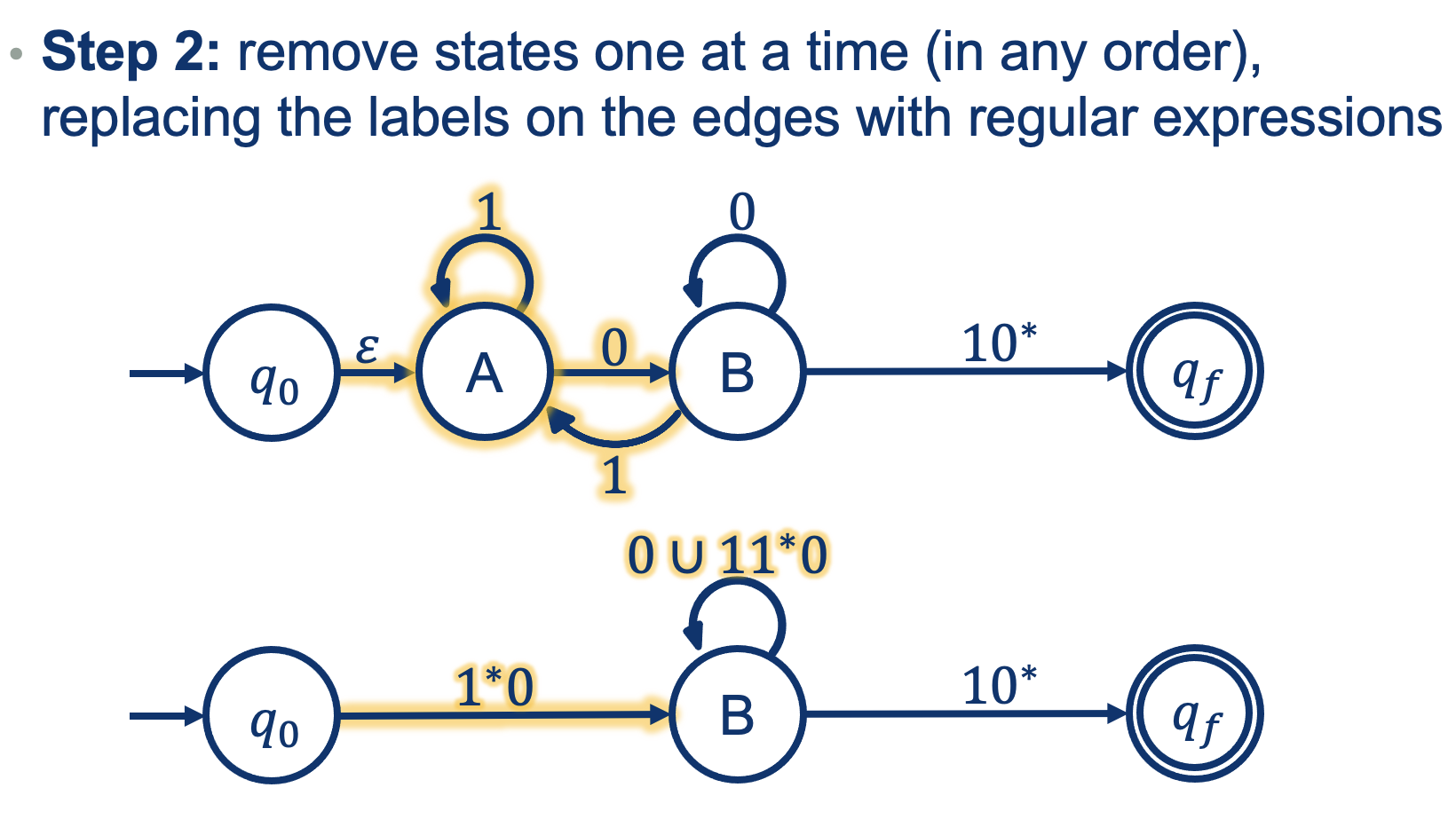
A more difficult one:
- To get into A: nothing to read
- Any numnber of 1s
- You need a 0 to get out
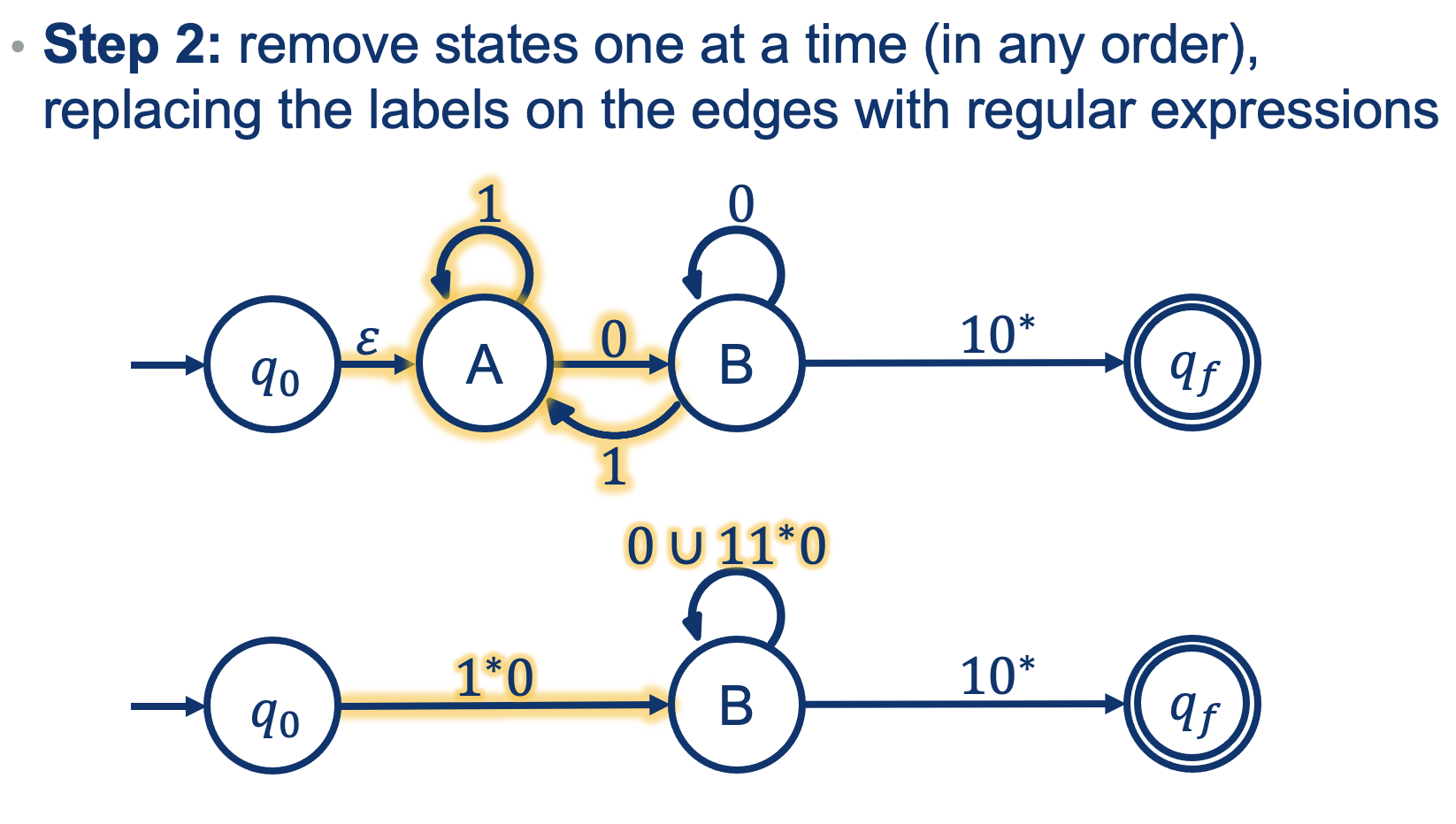
But removing A also changes B!
I need to accont for the transitions going back and forth between A and B!
So how could one get into B?
- We could read a 0 to get into B, OR
- Read a 1 from inside B, read any number of 1s while at A, and then a 0 to get back to B
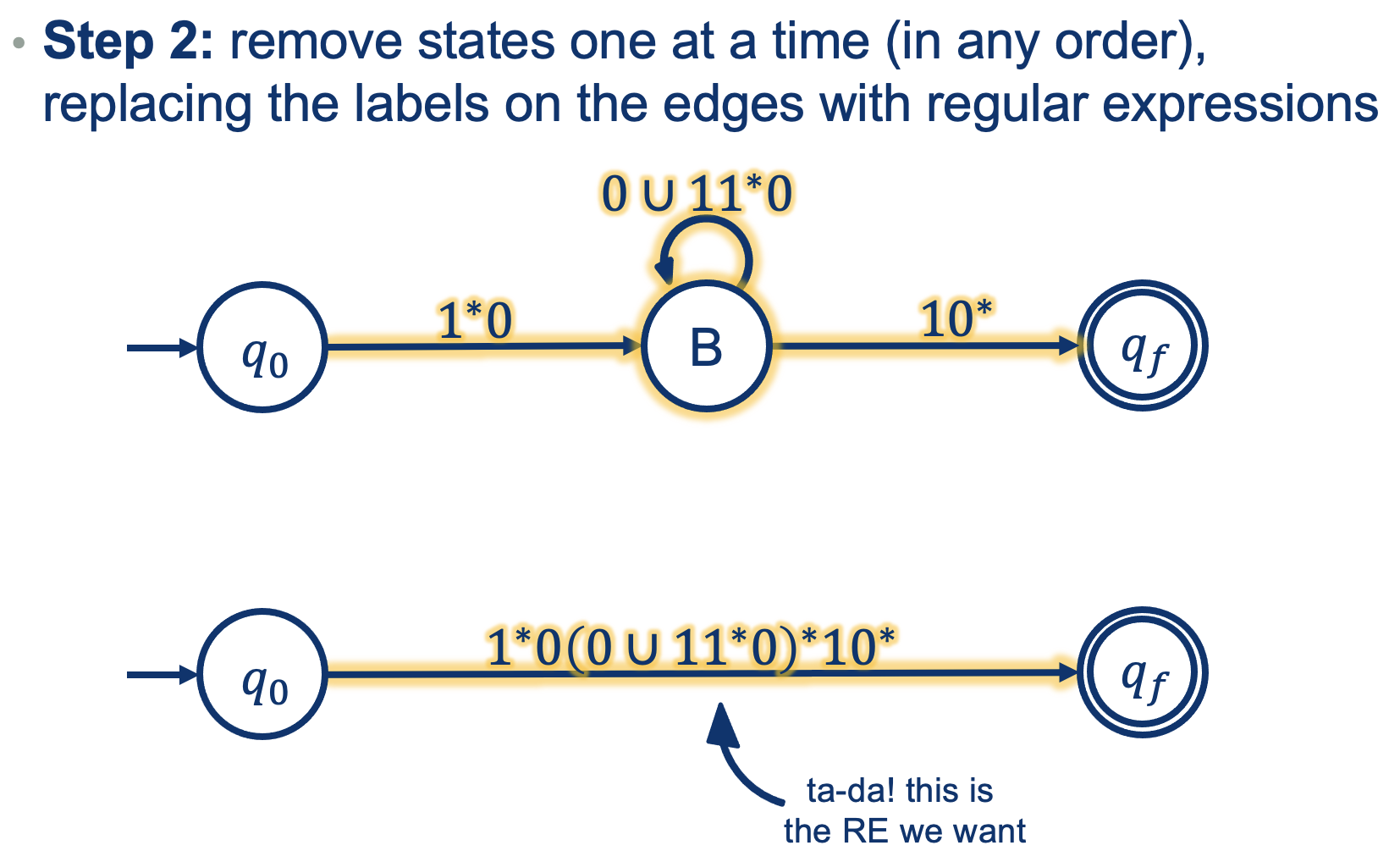
So What did we prove?