CSC 102
How The Internet Works
Smith Computer Science
How The Internet Works
Smith Computer Science







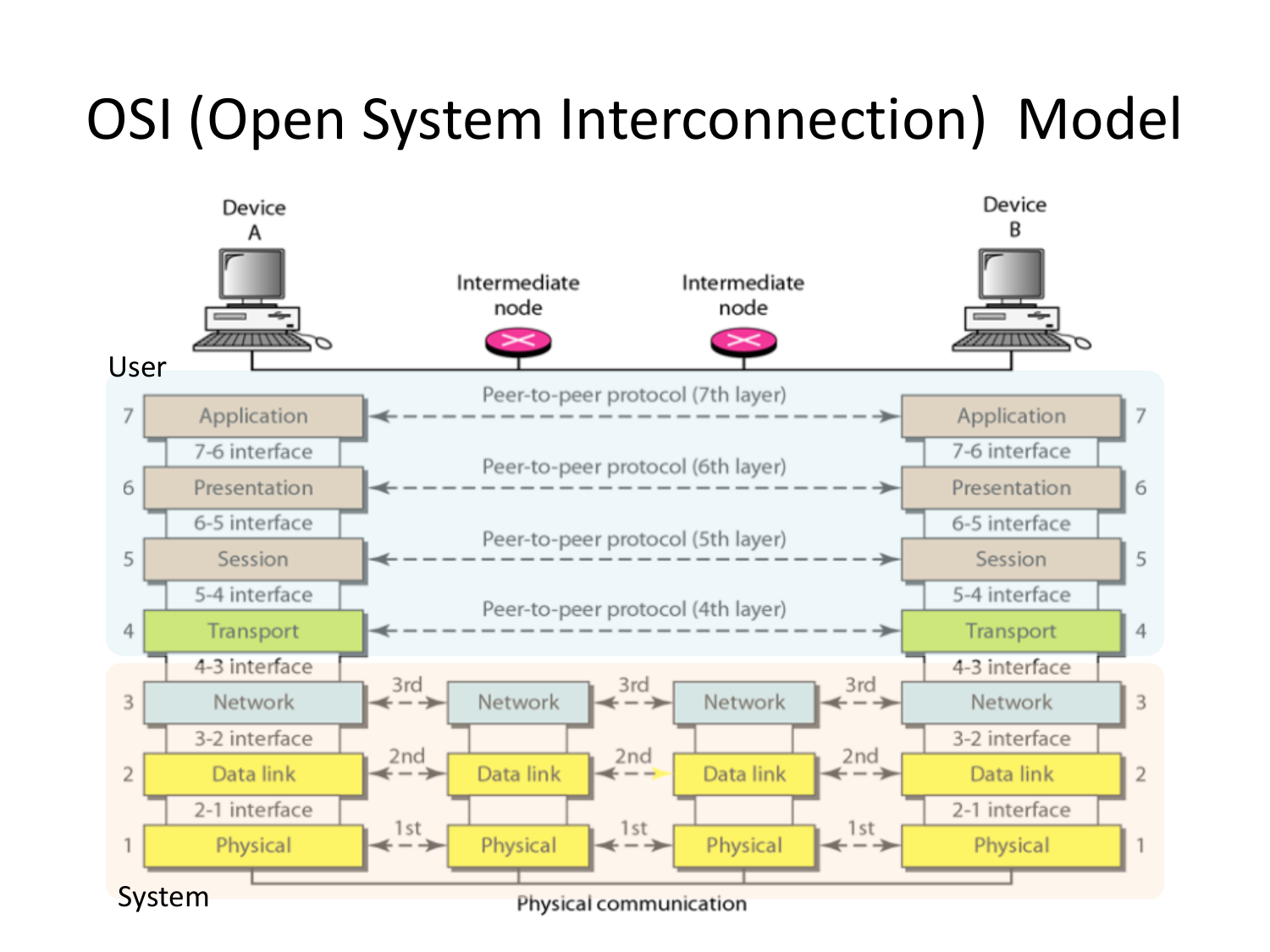
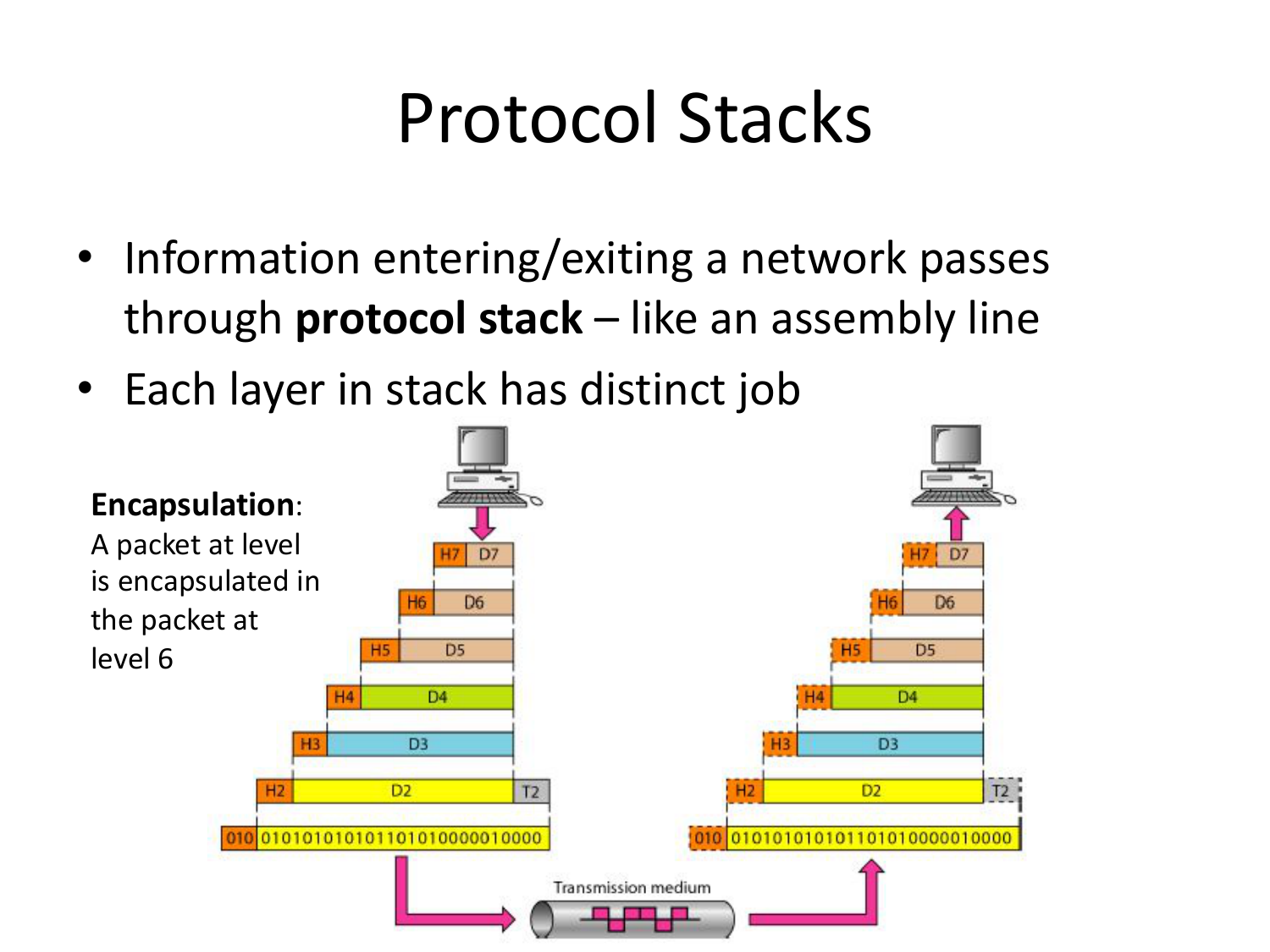

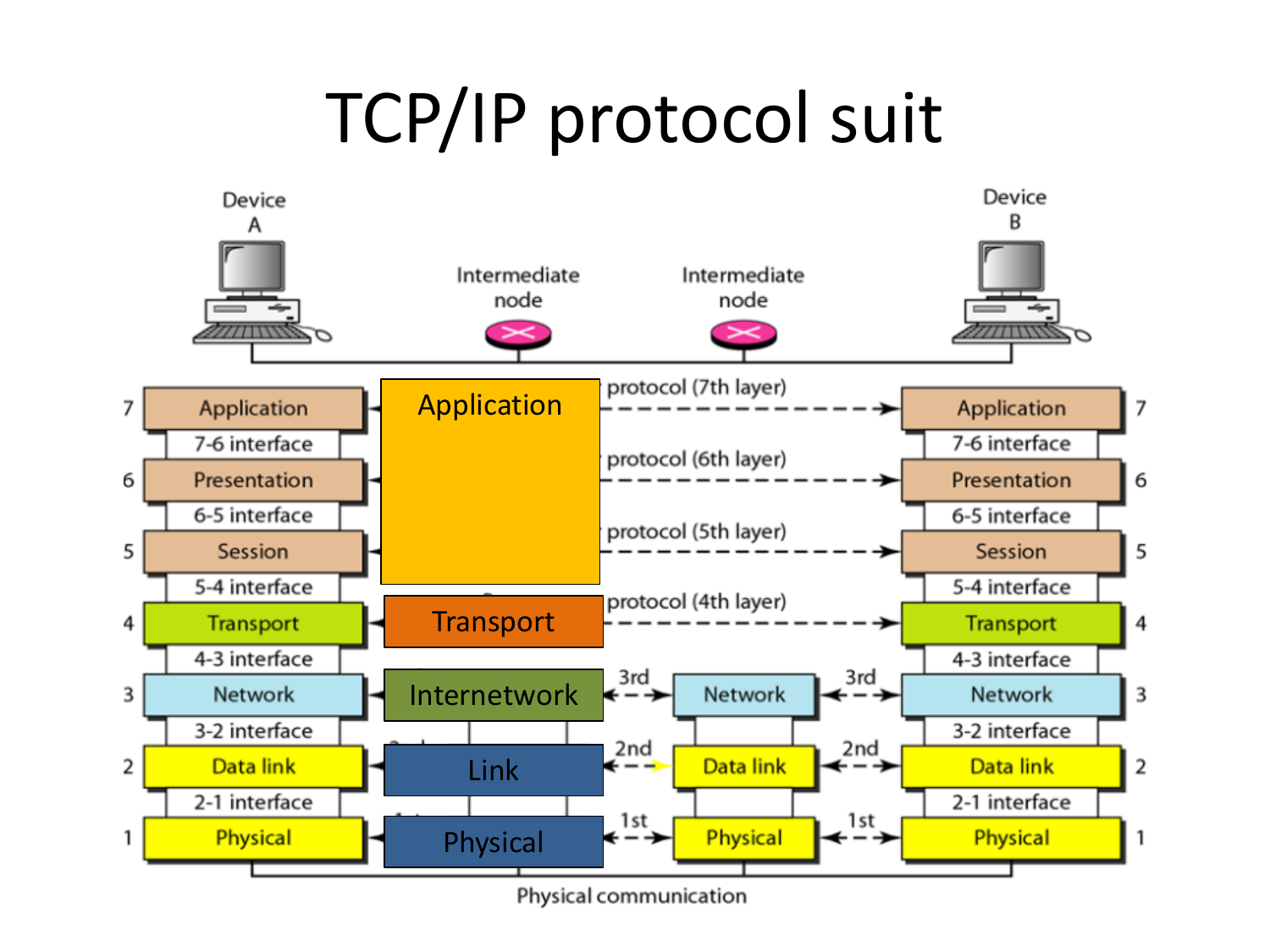
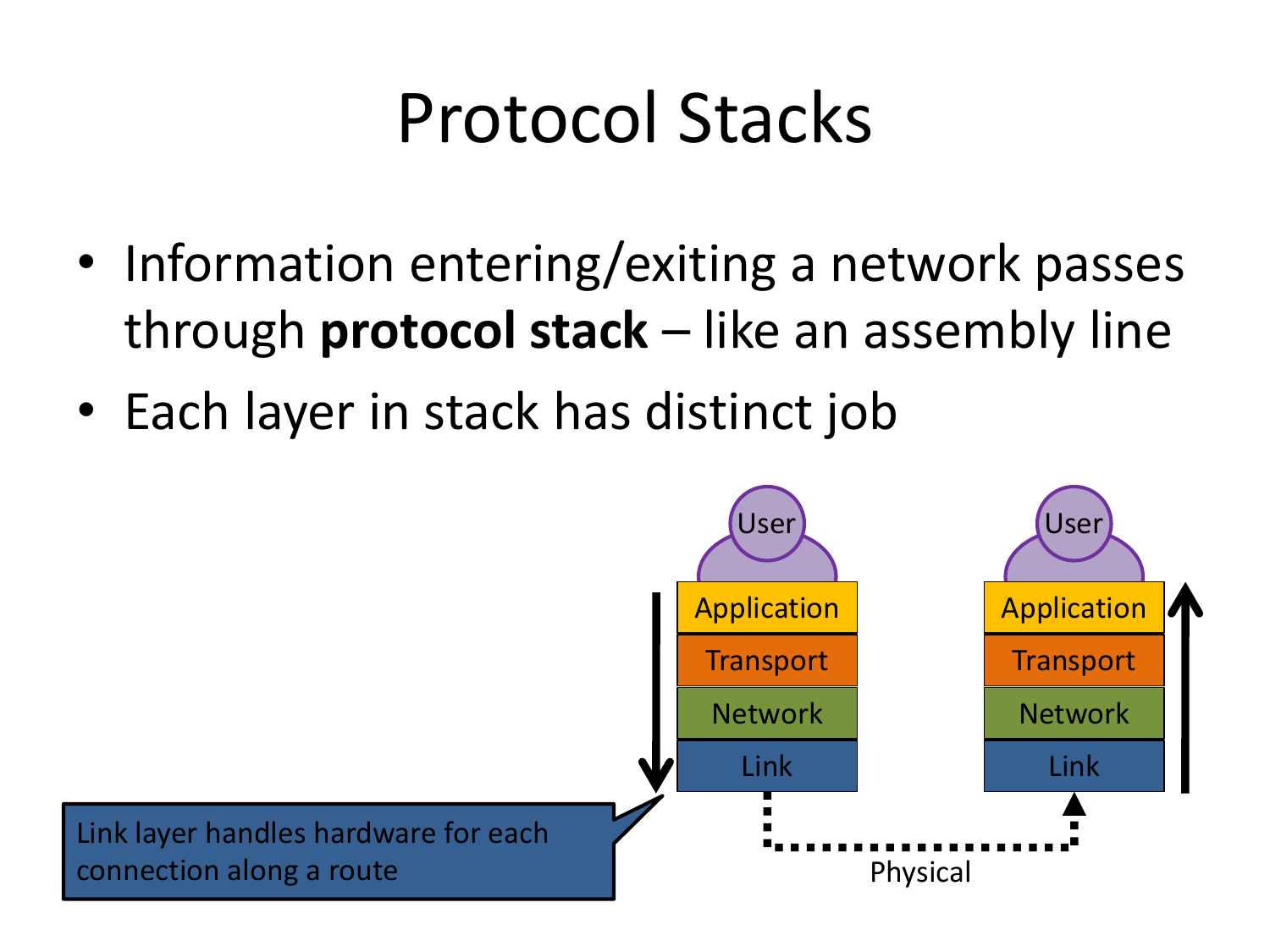
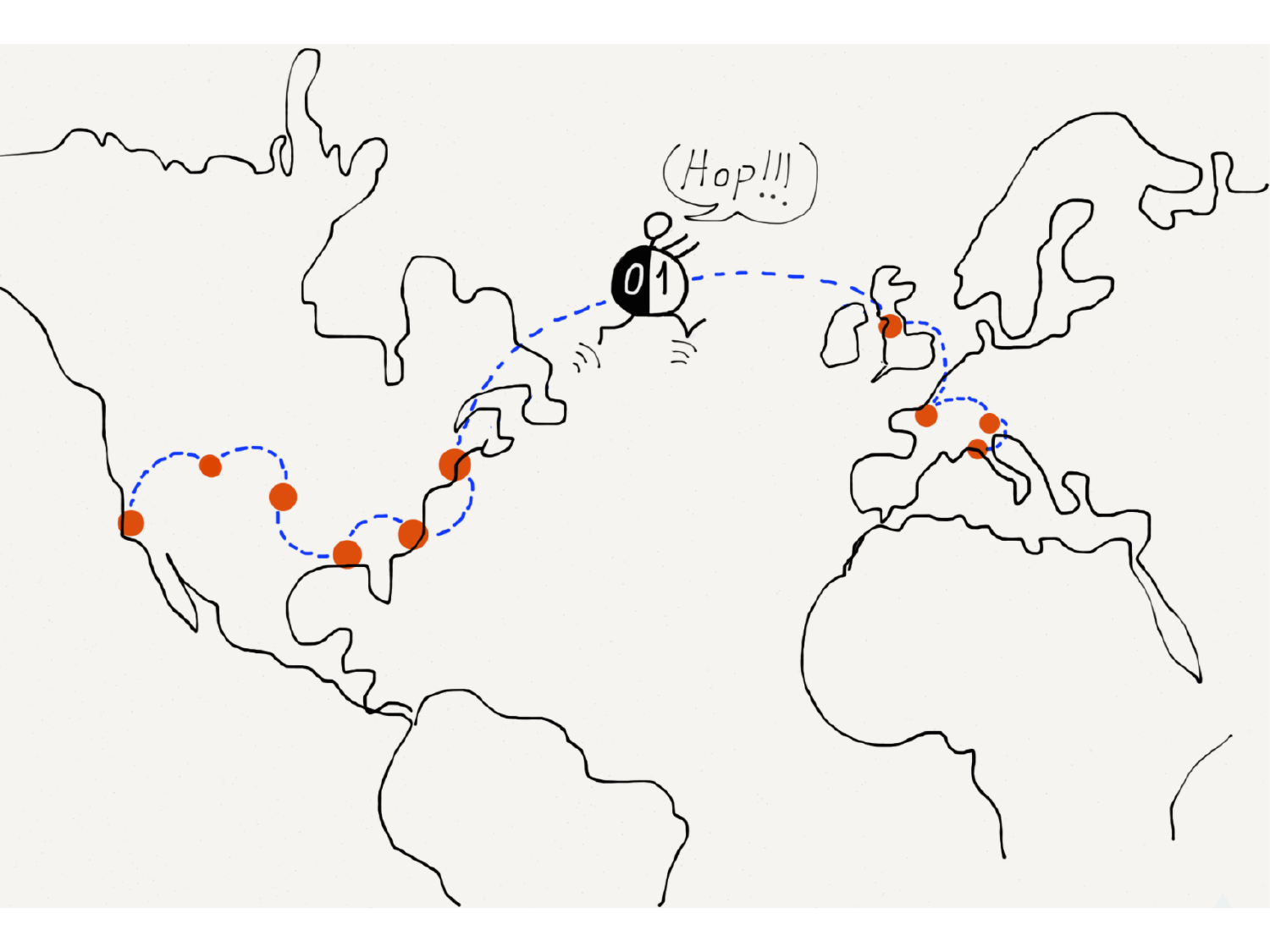
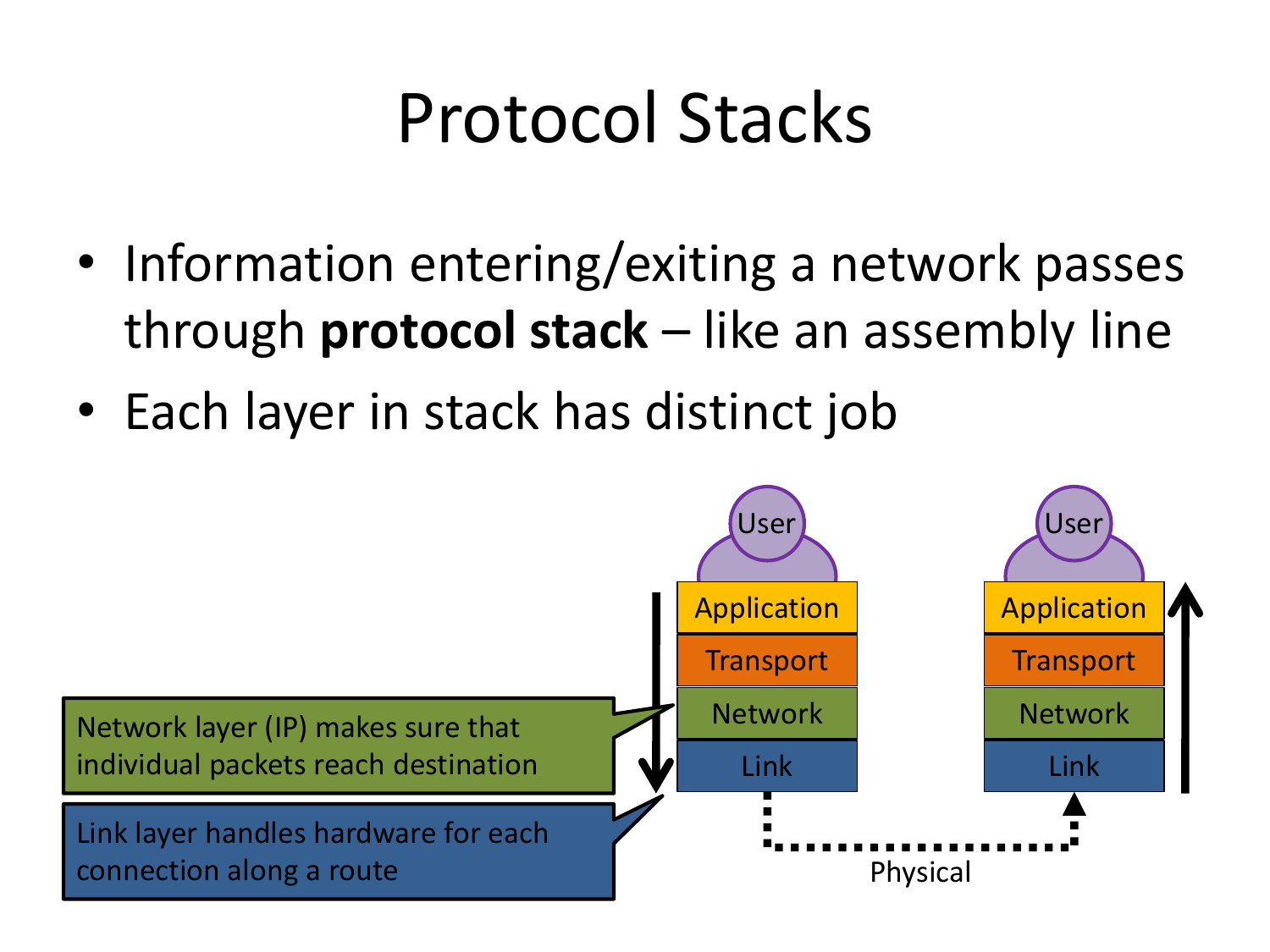
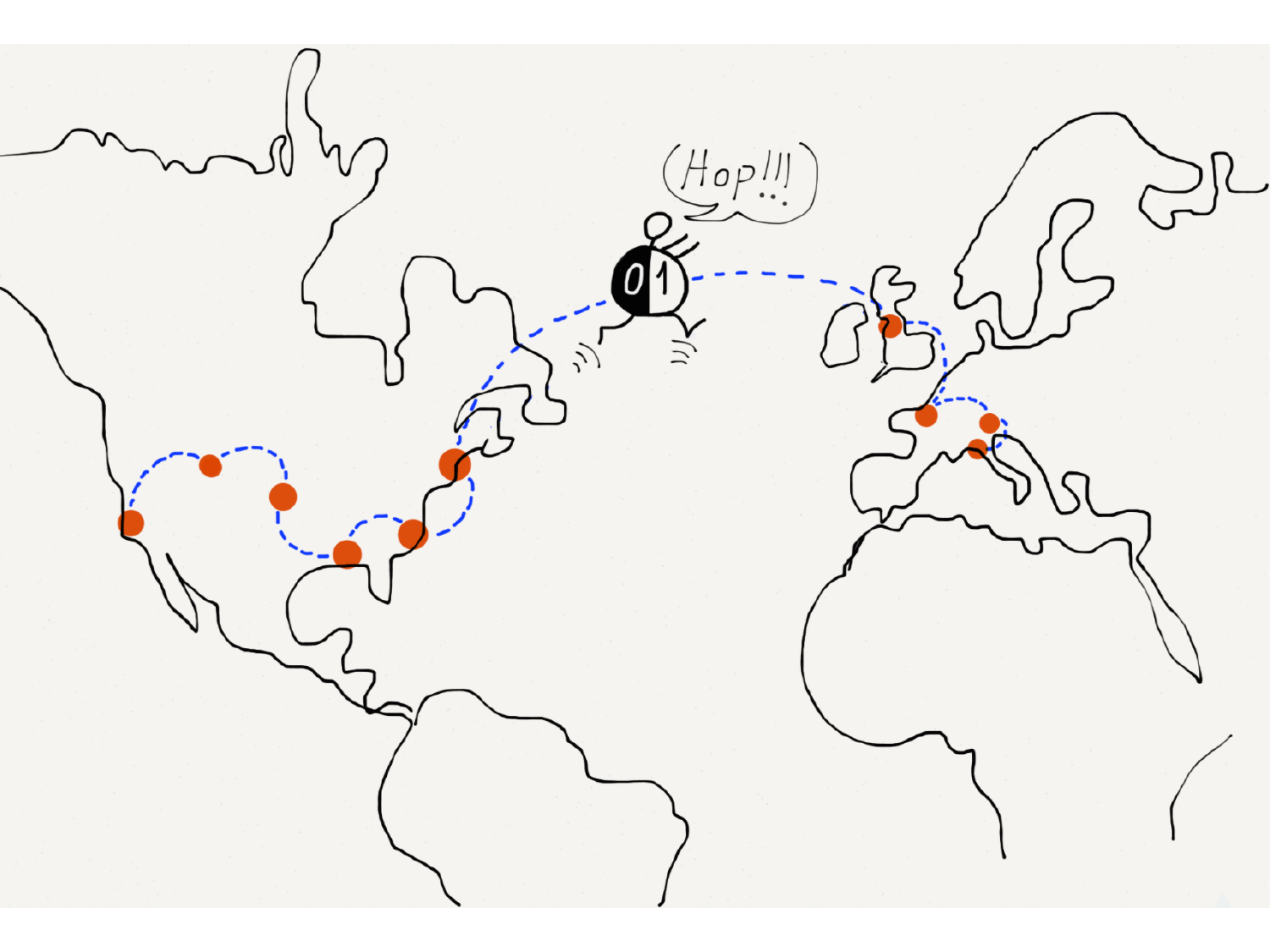
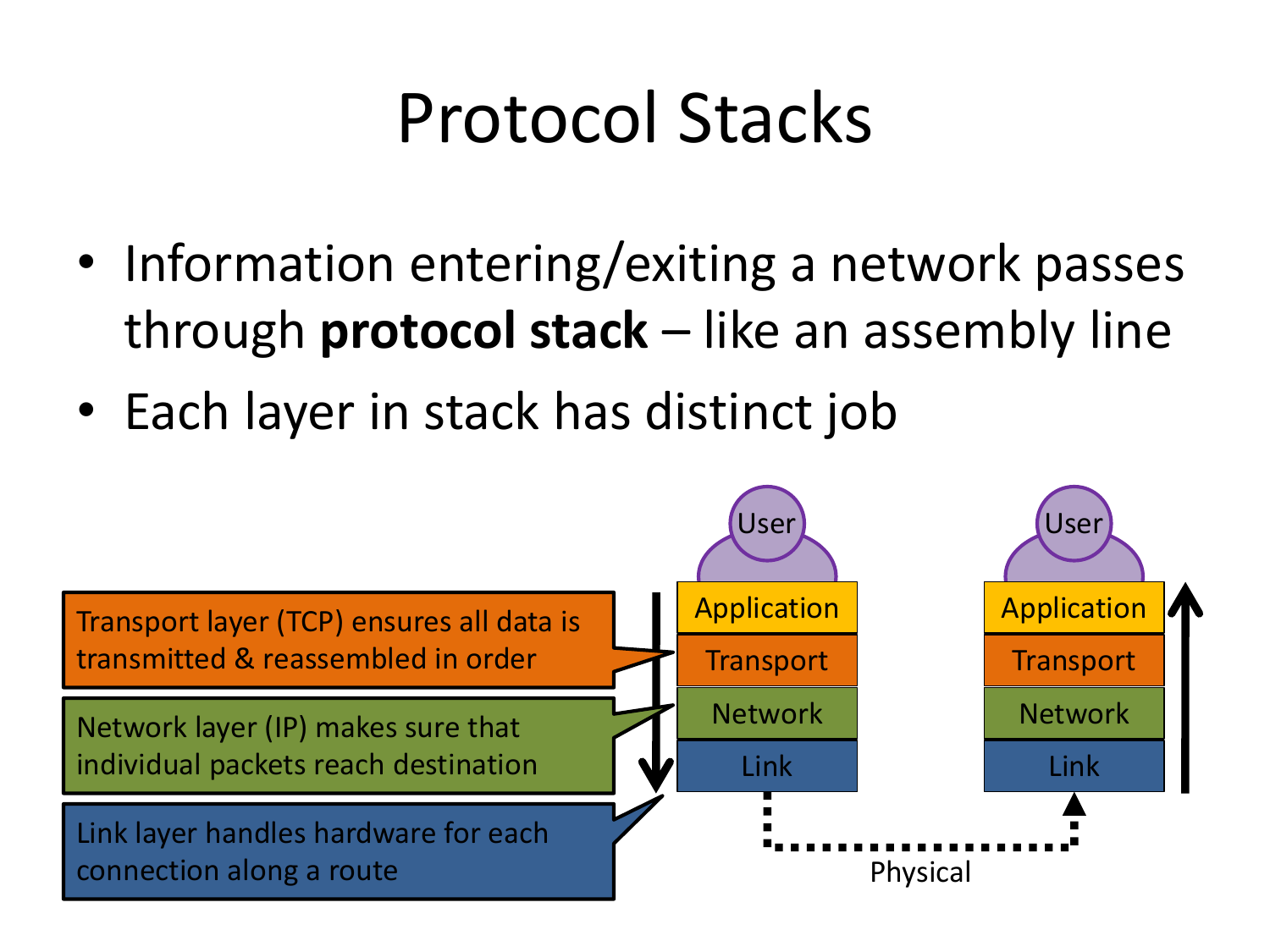
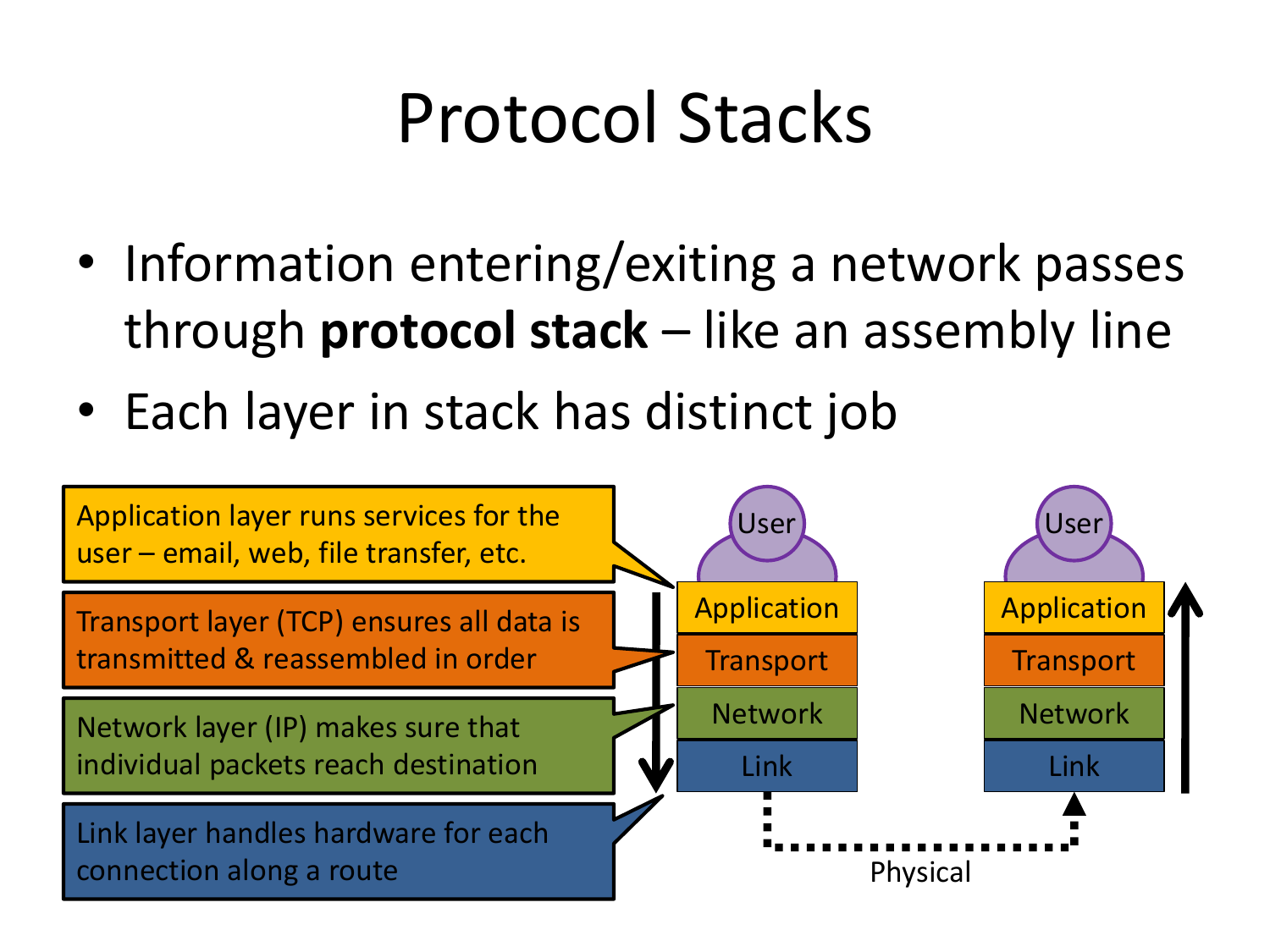
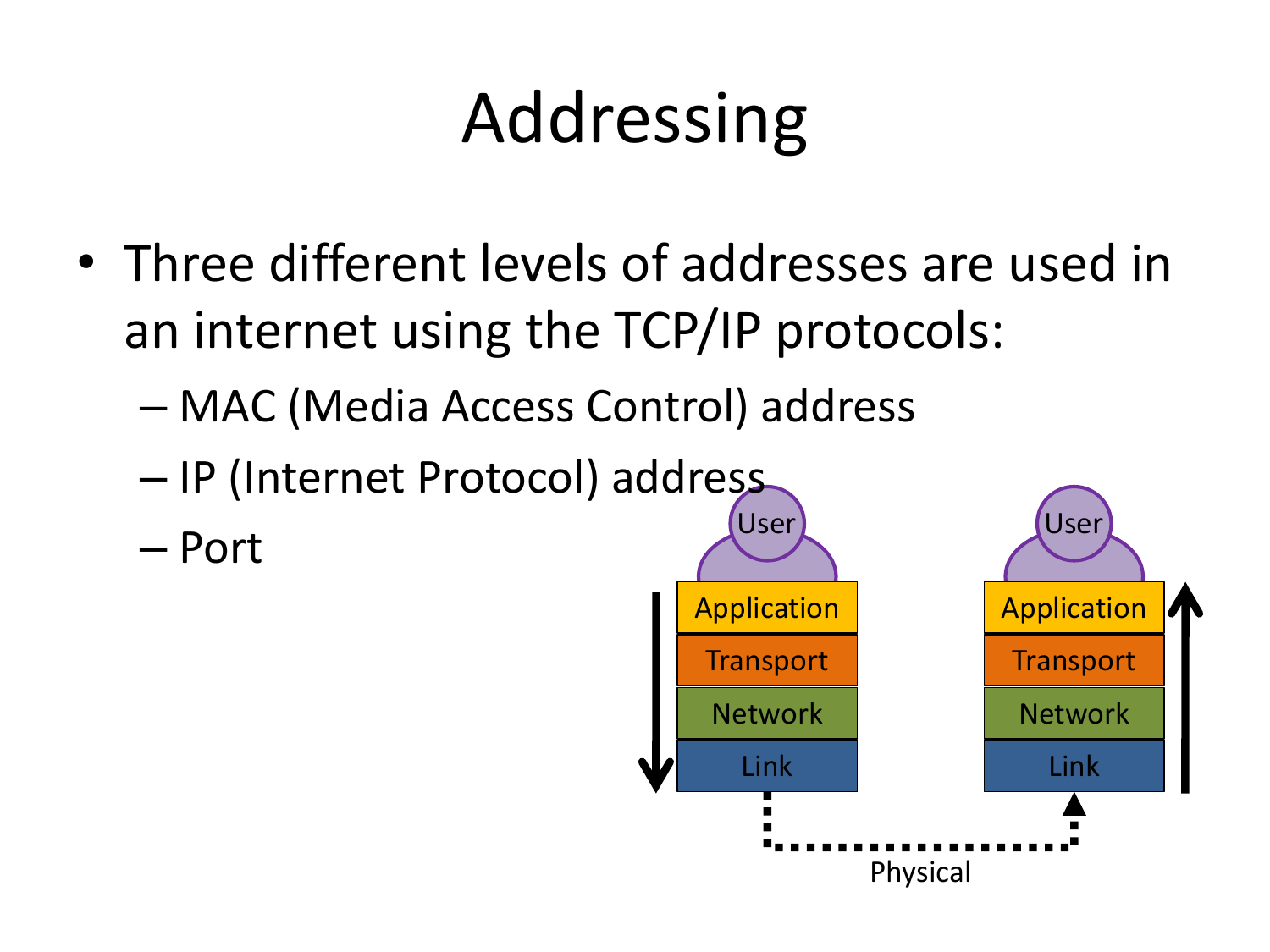
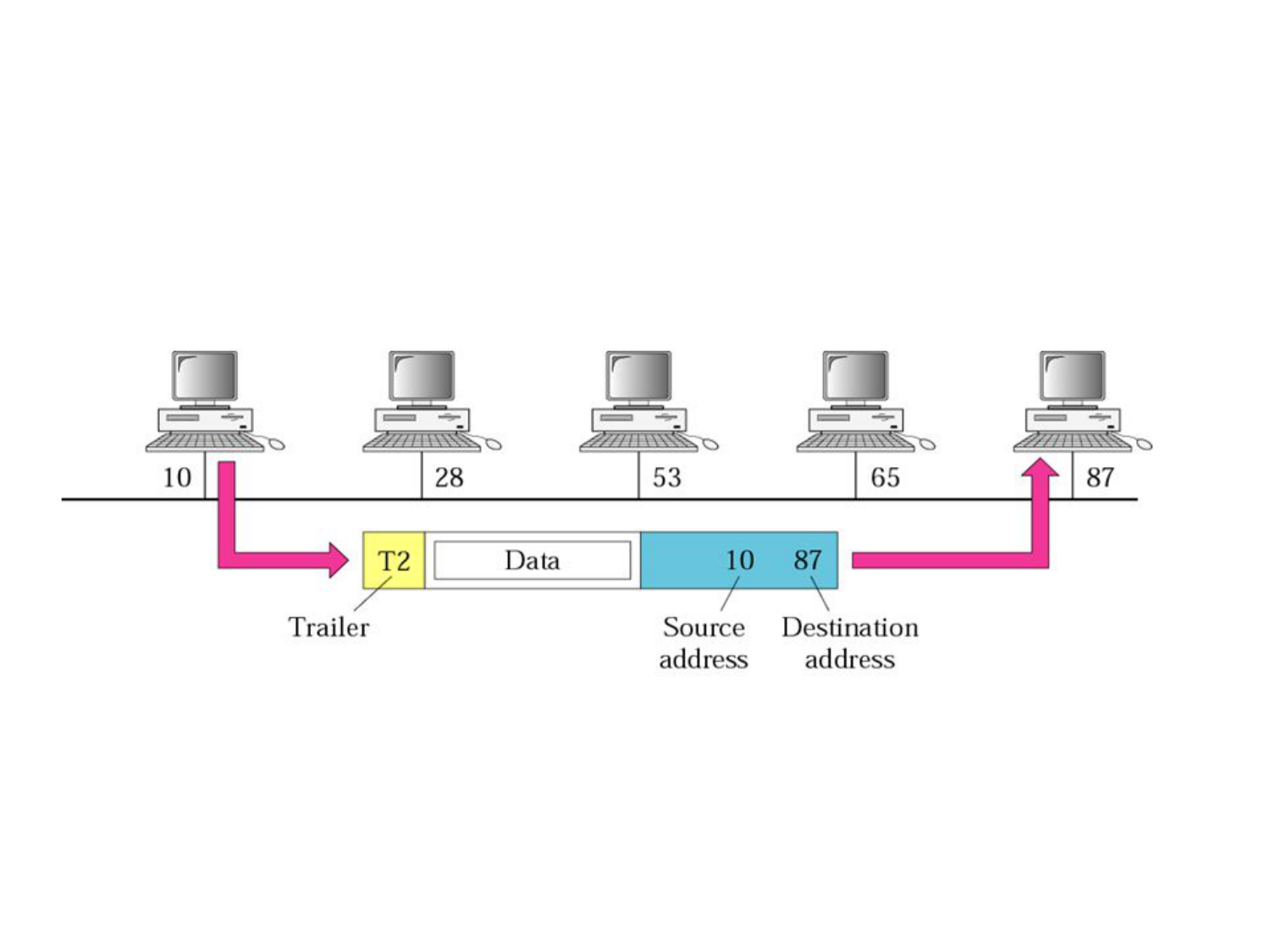
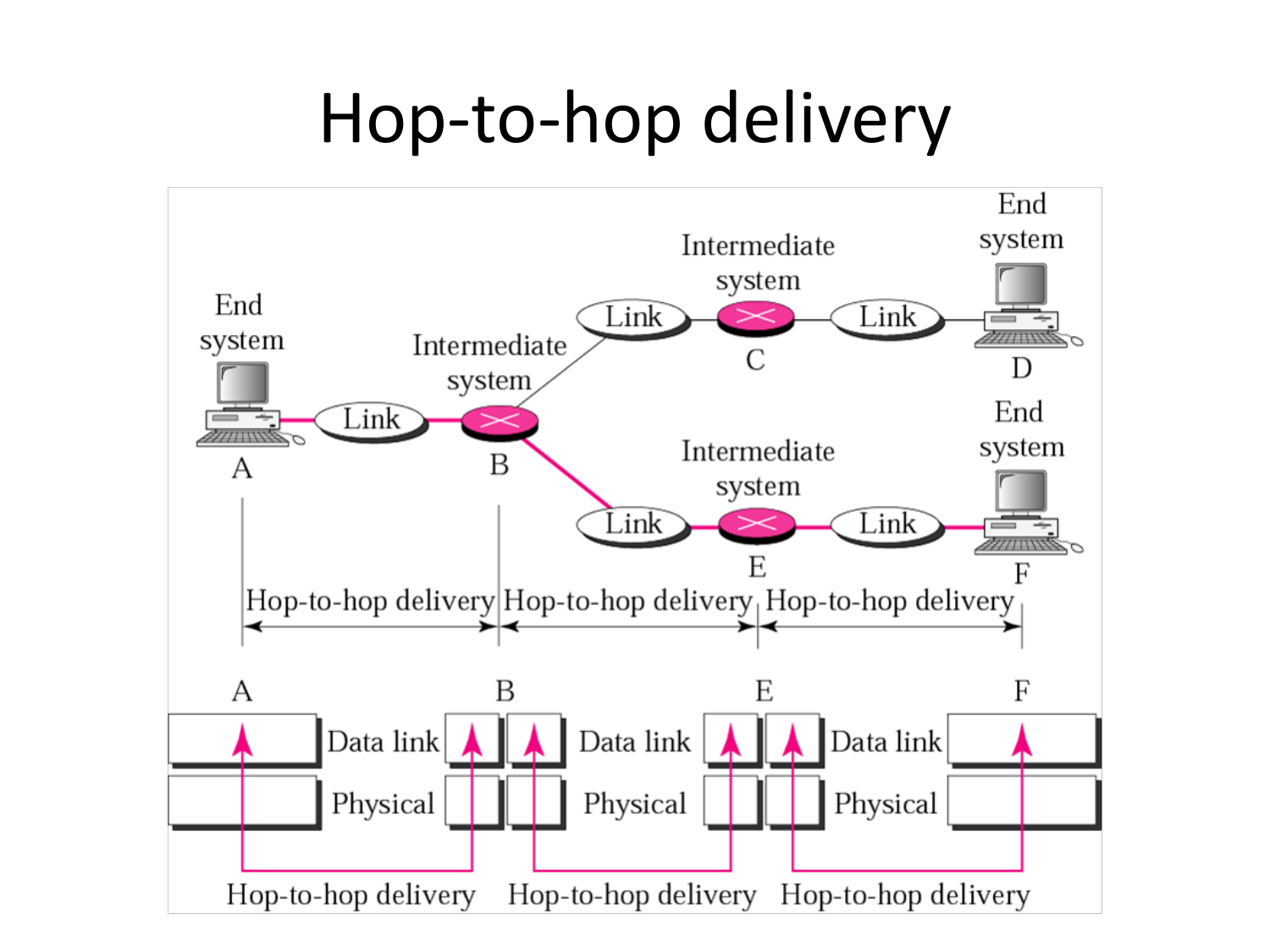
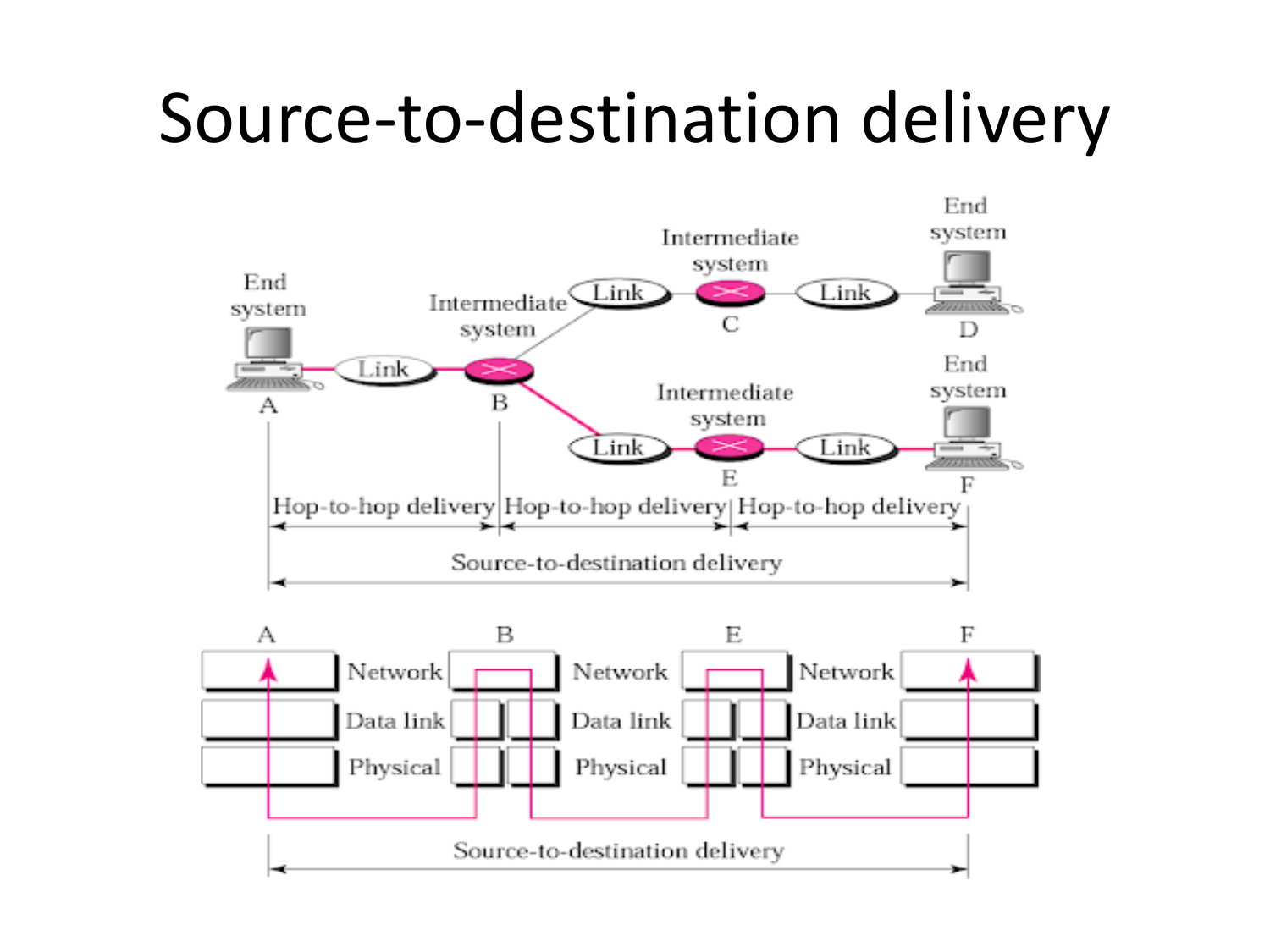


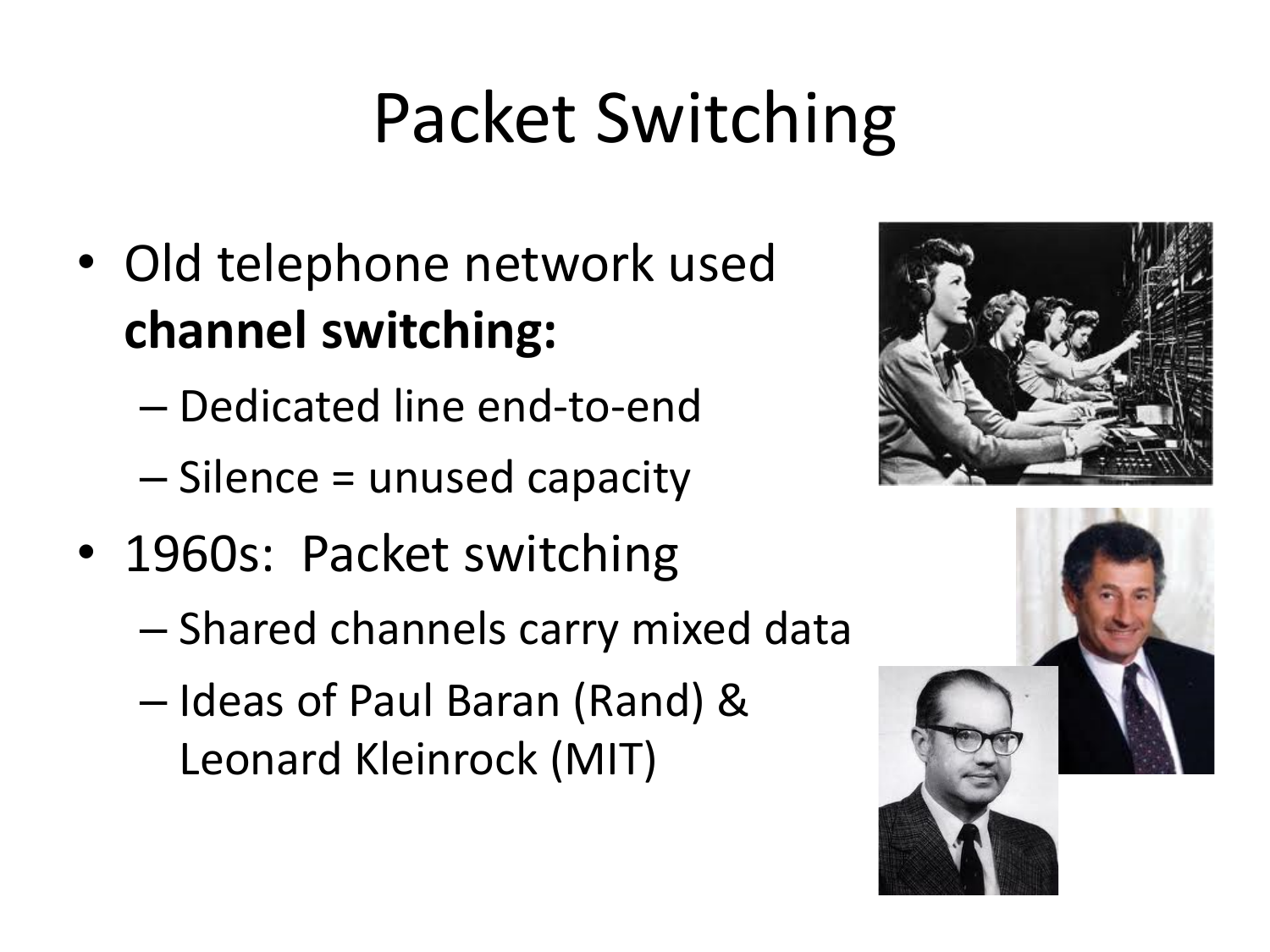
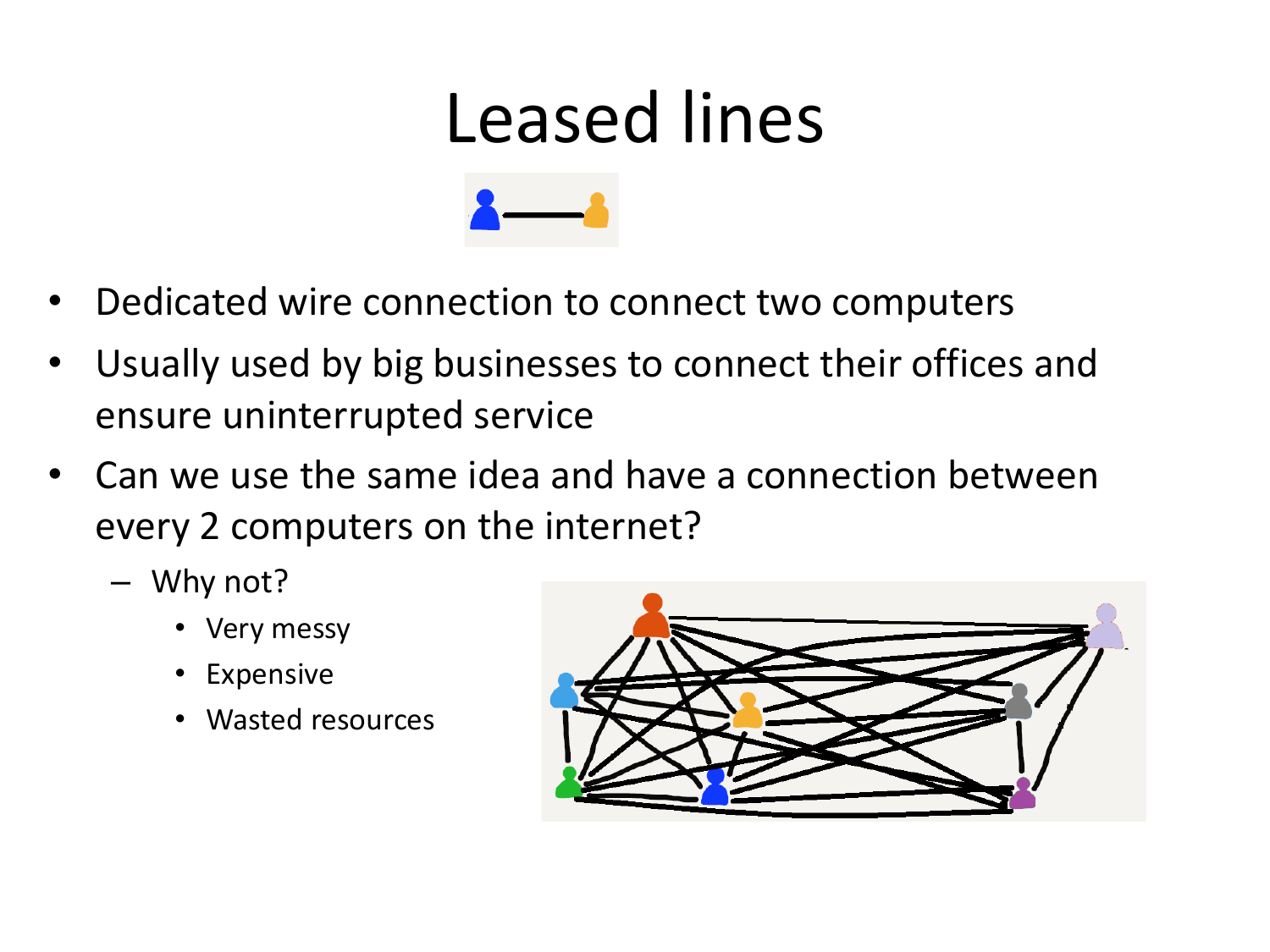
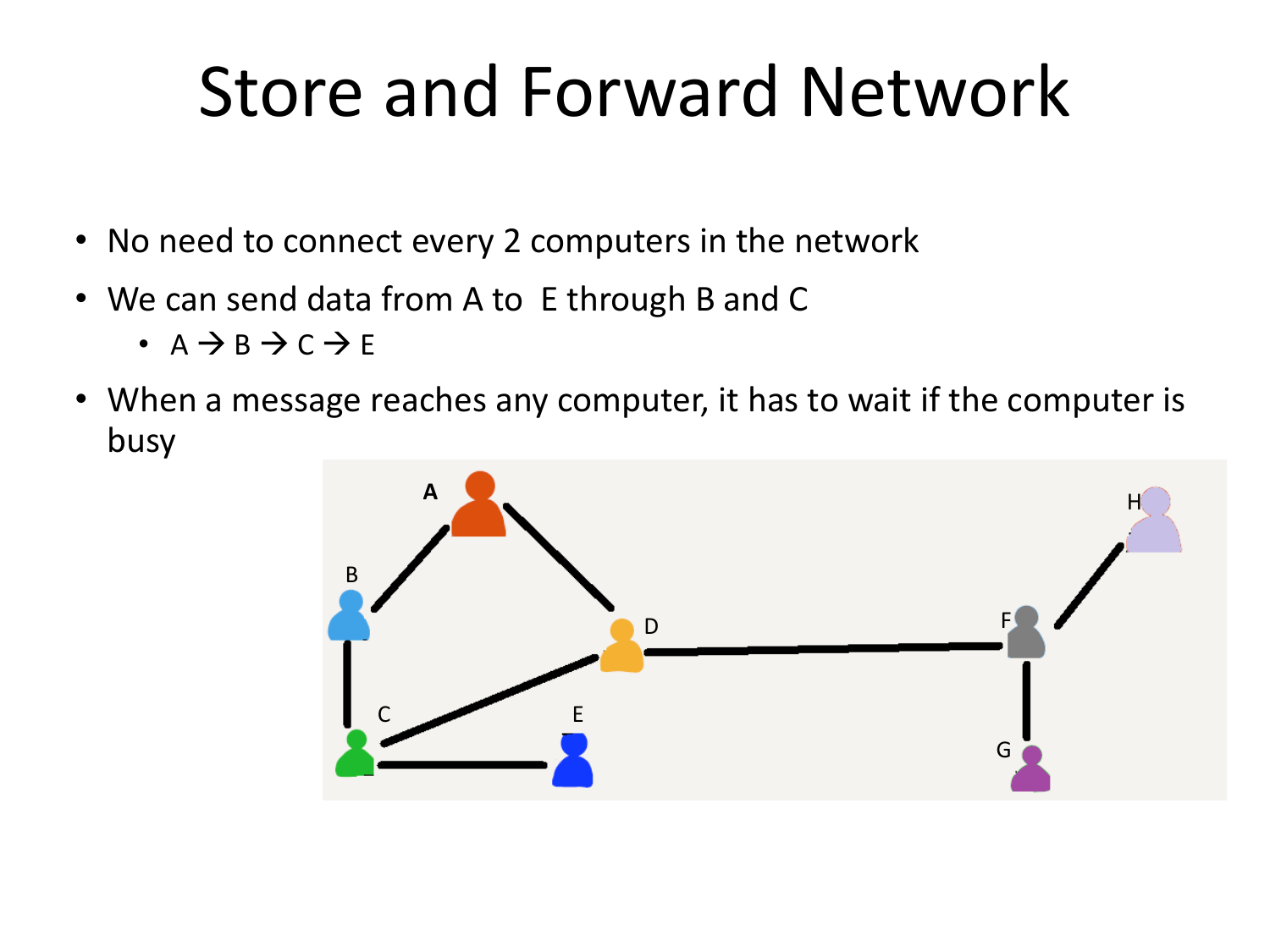
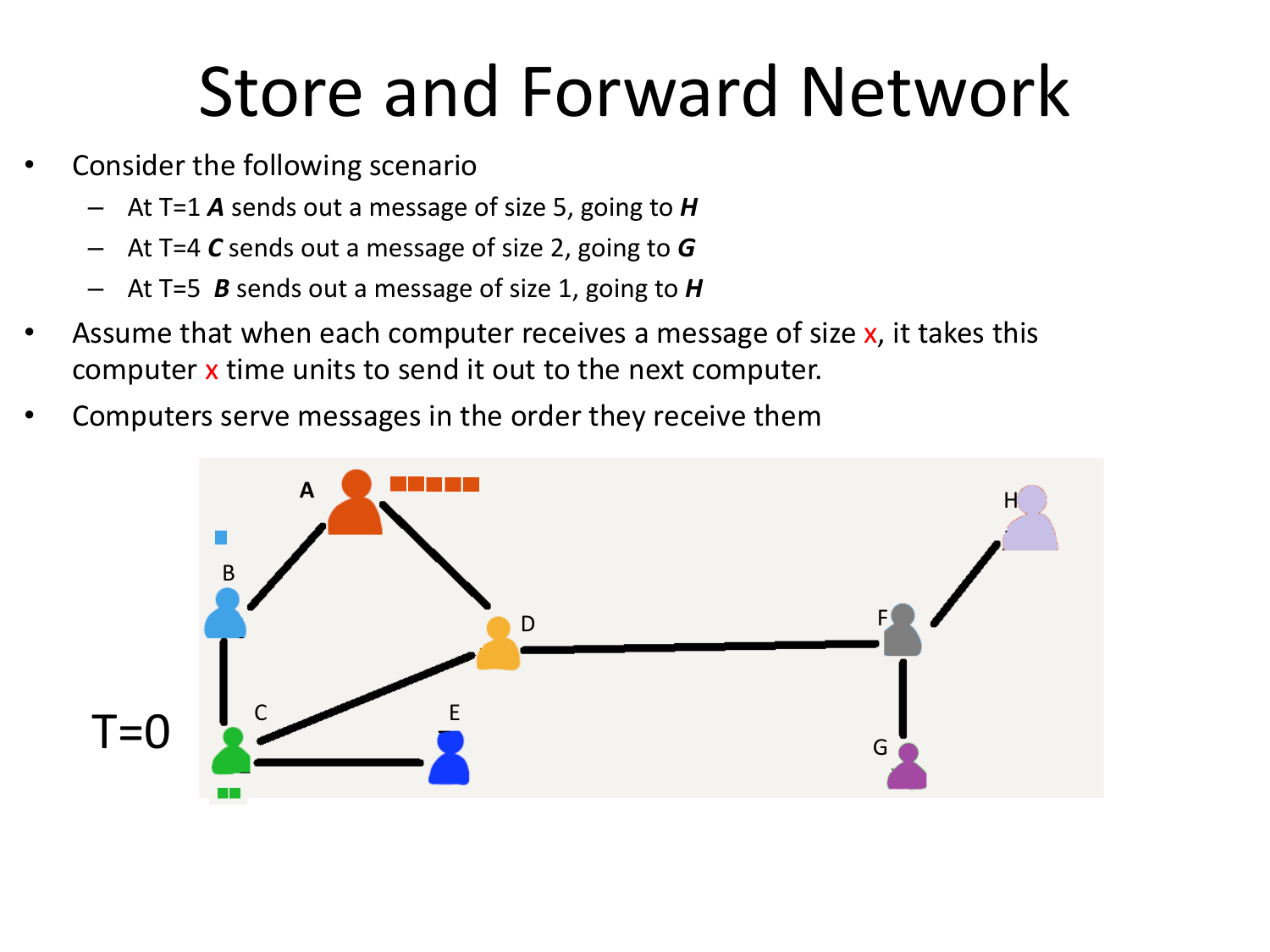
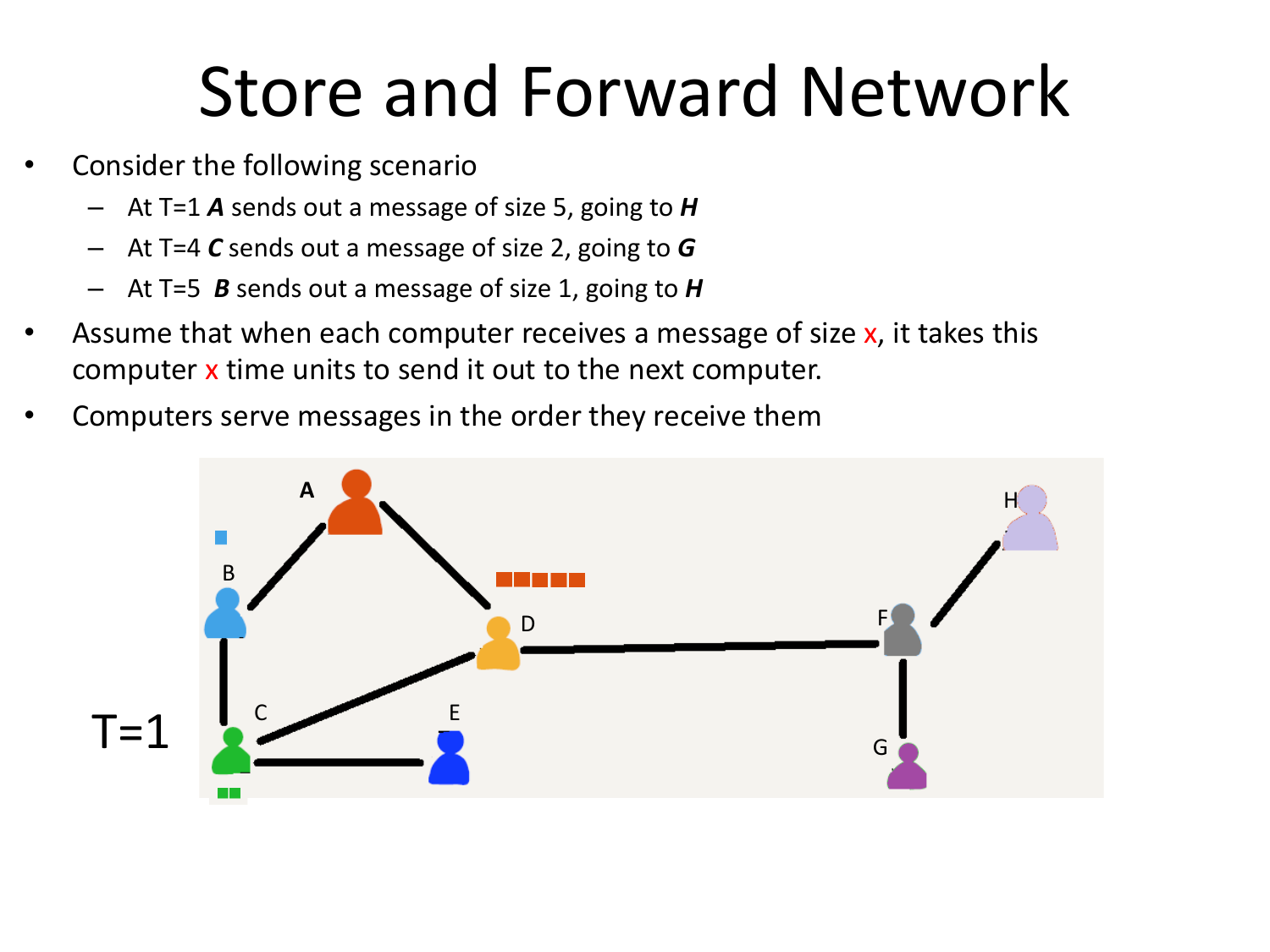
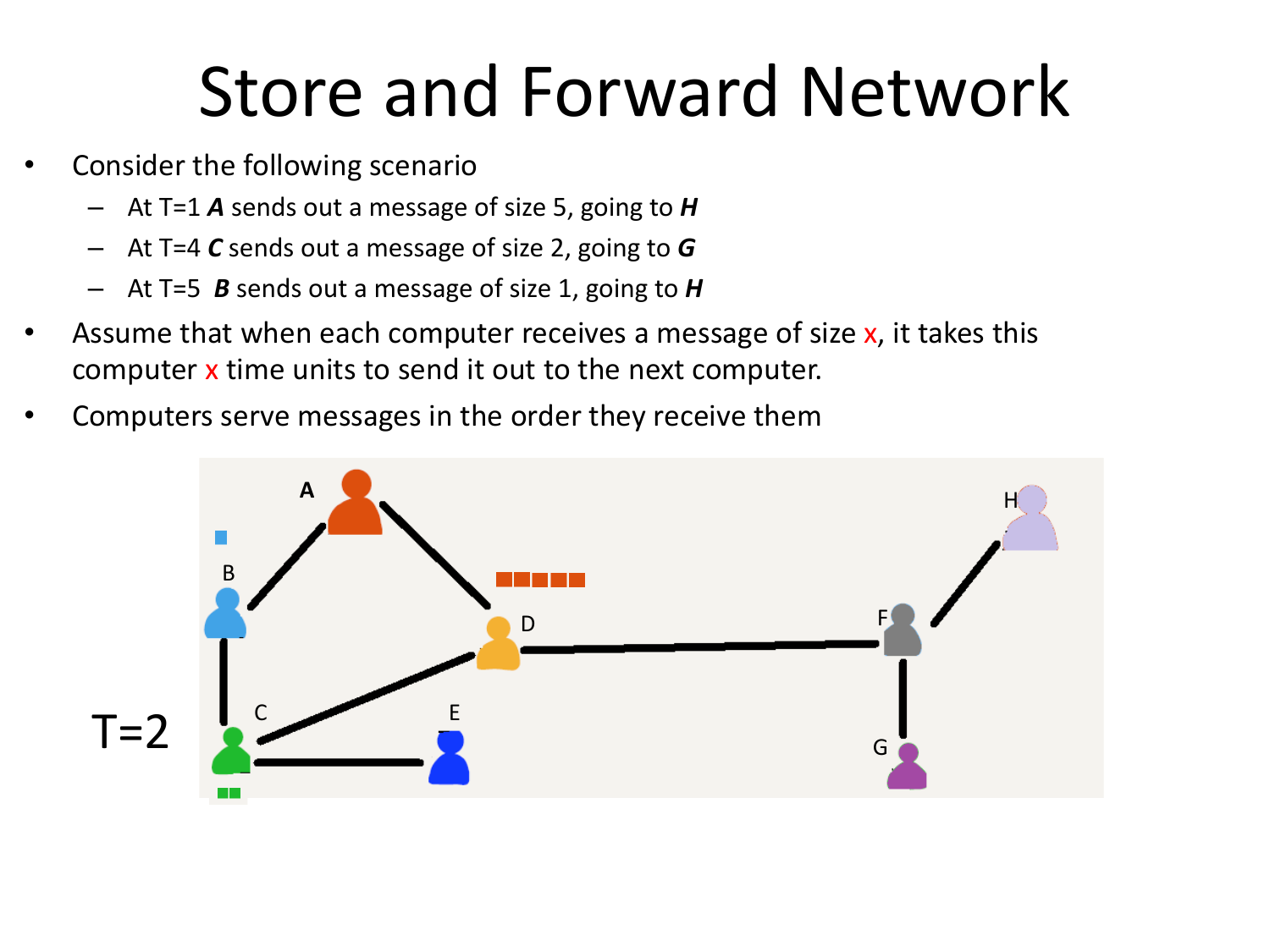
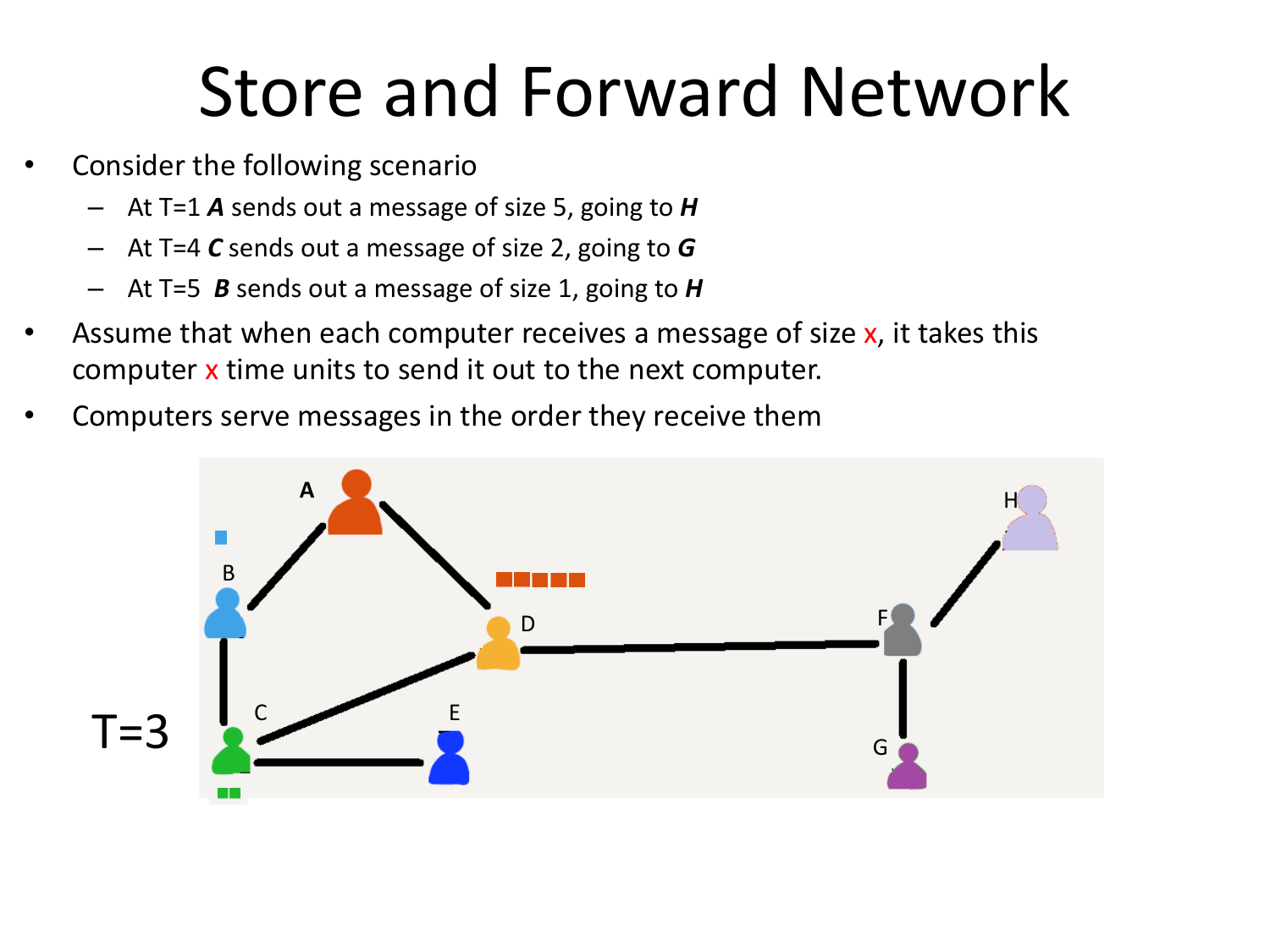
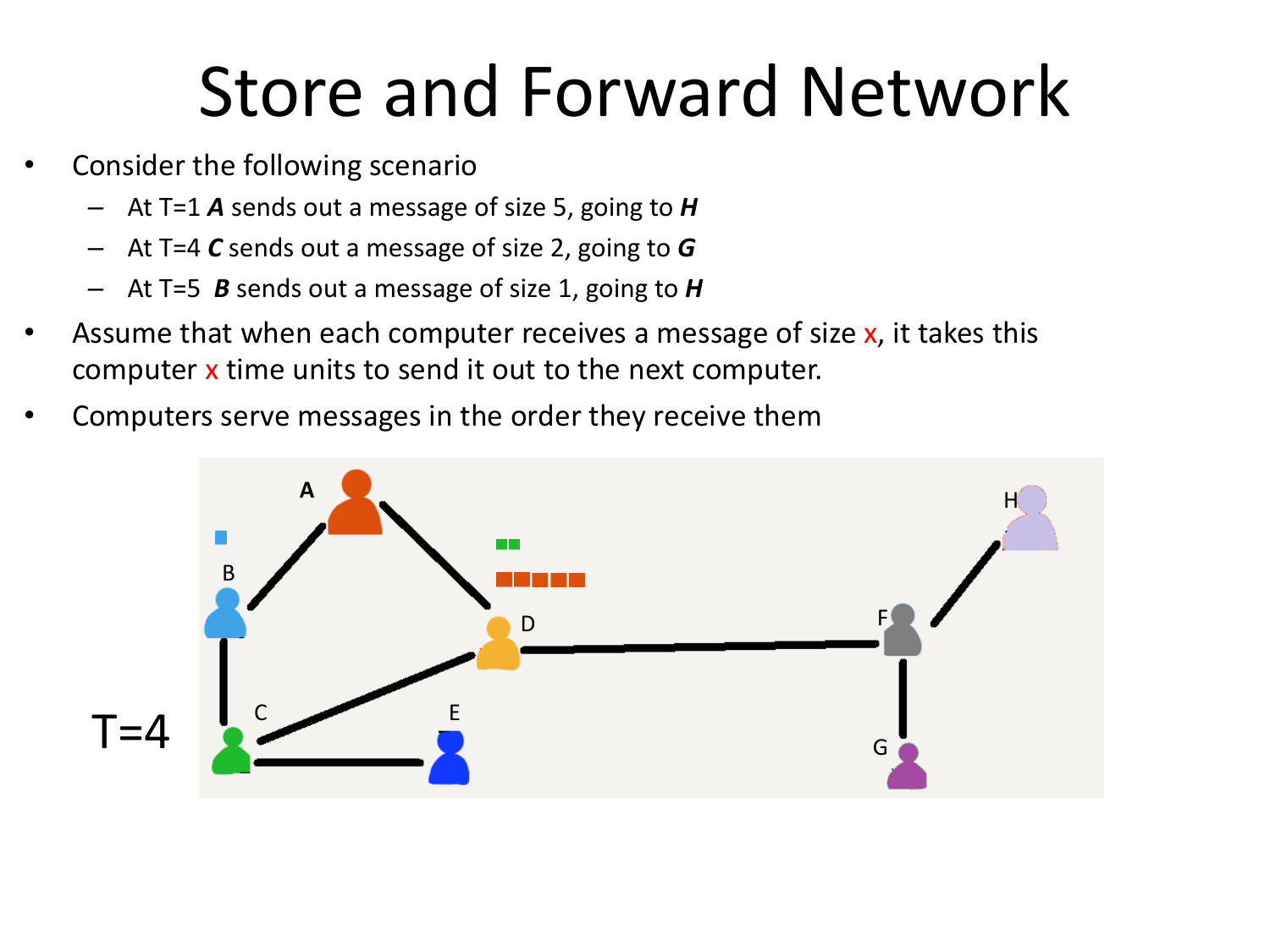
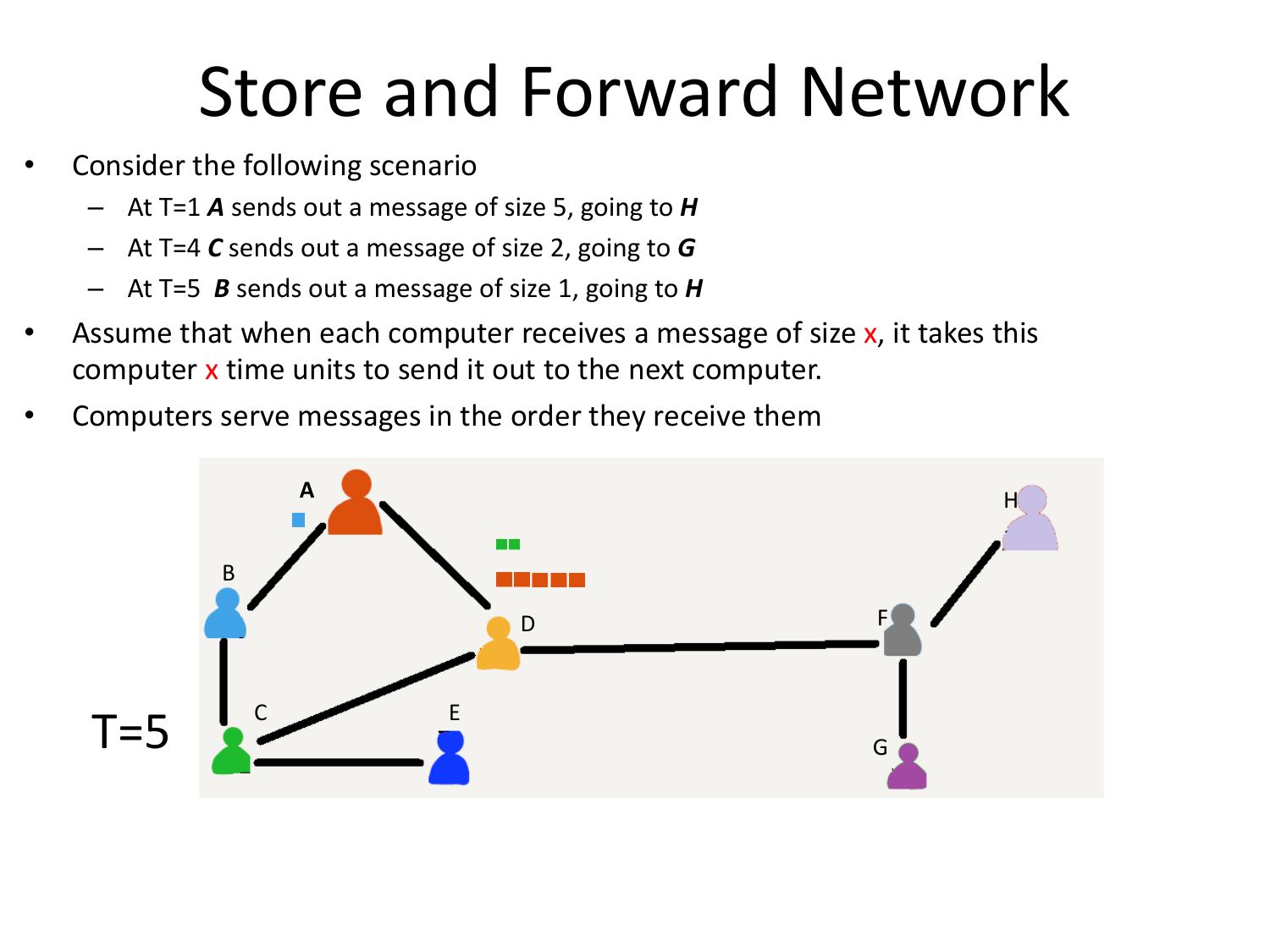
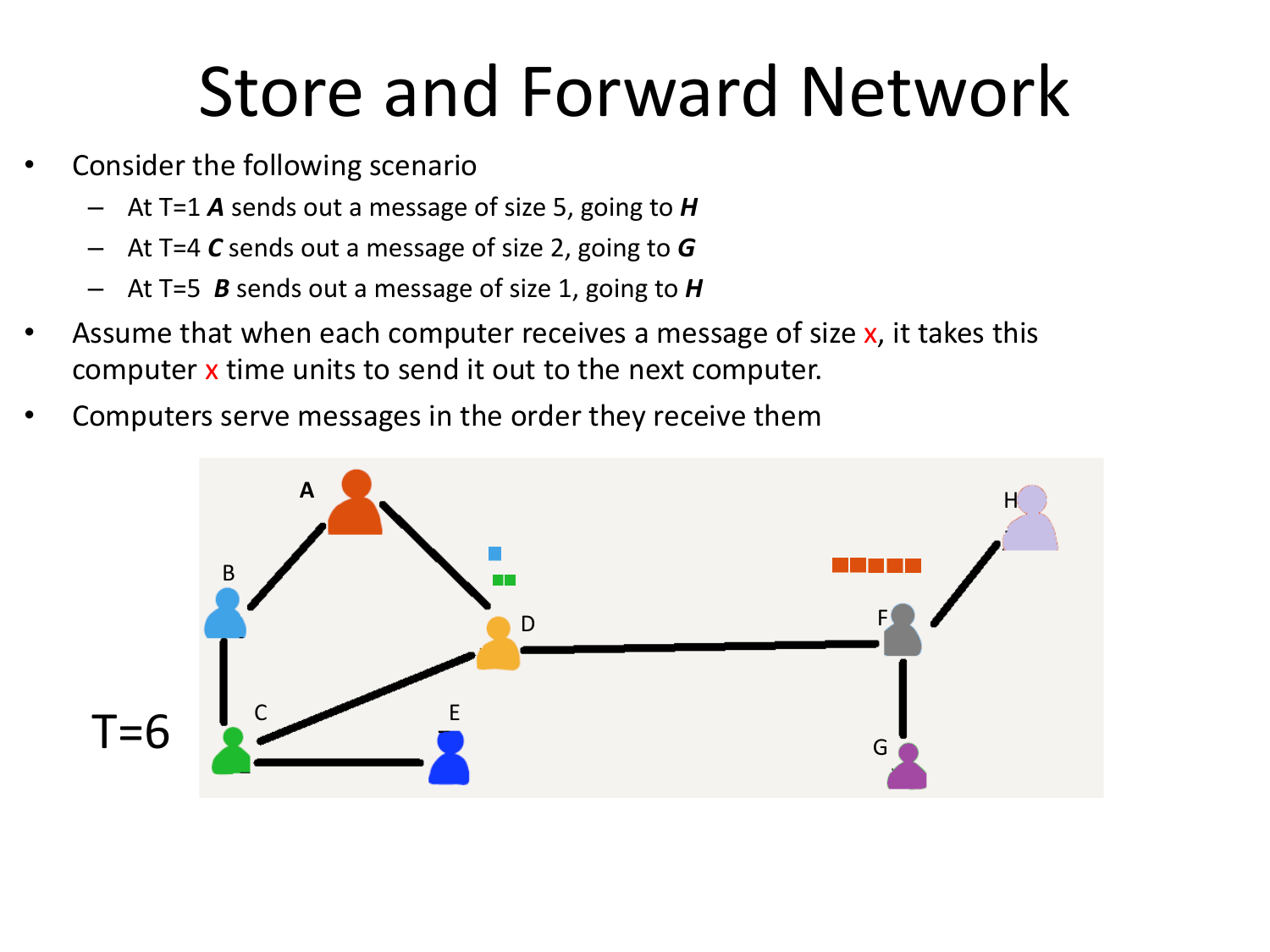
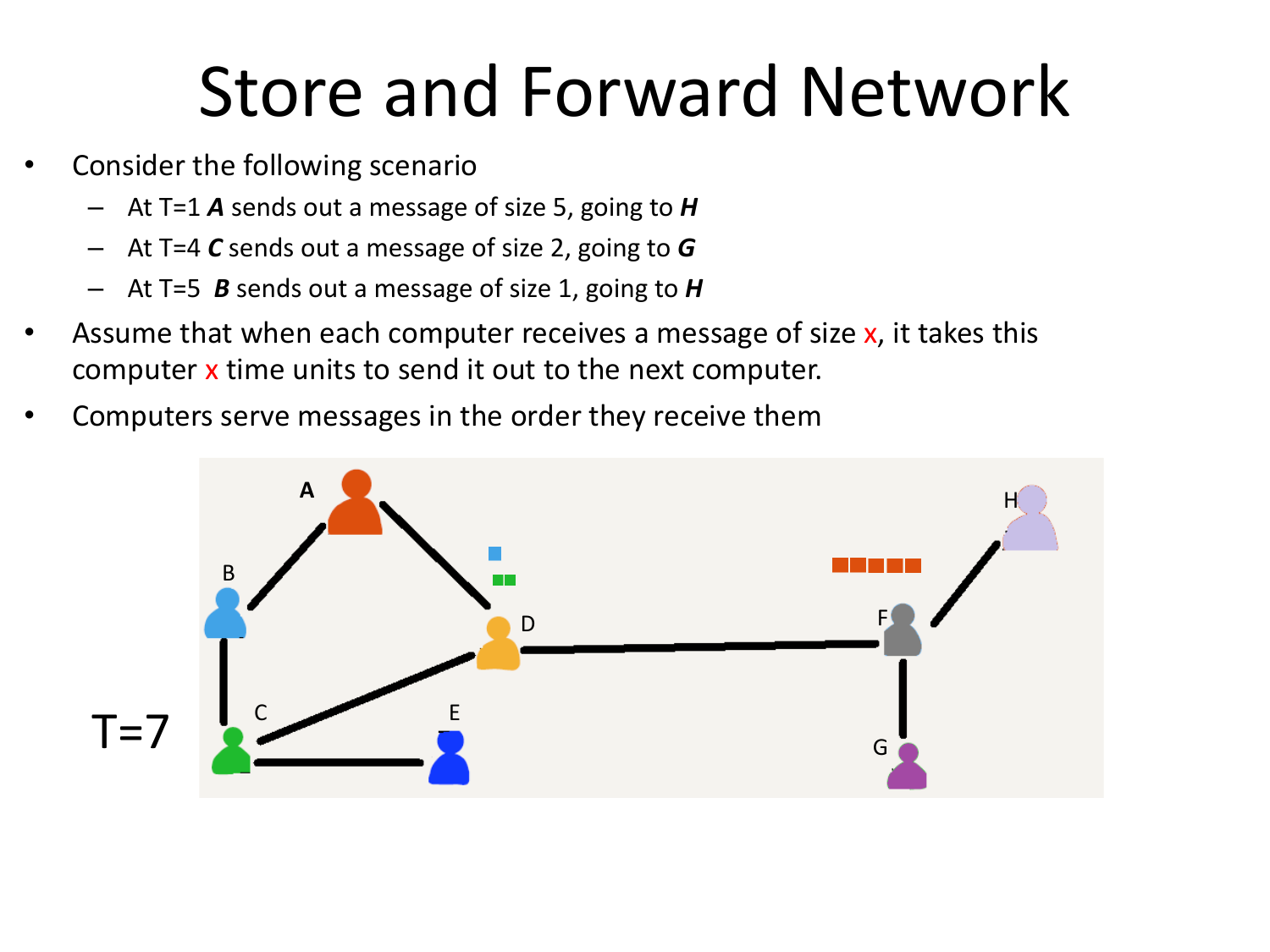
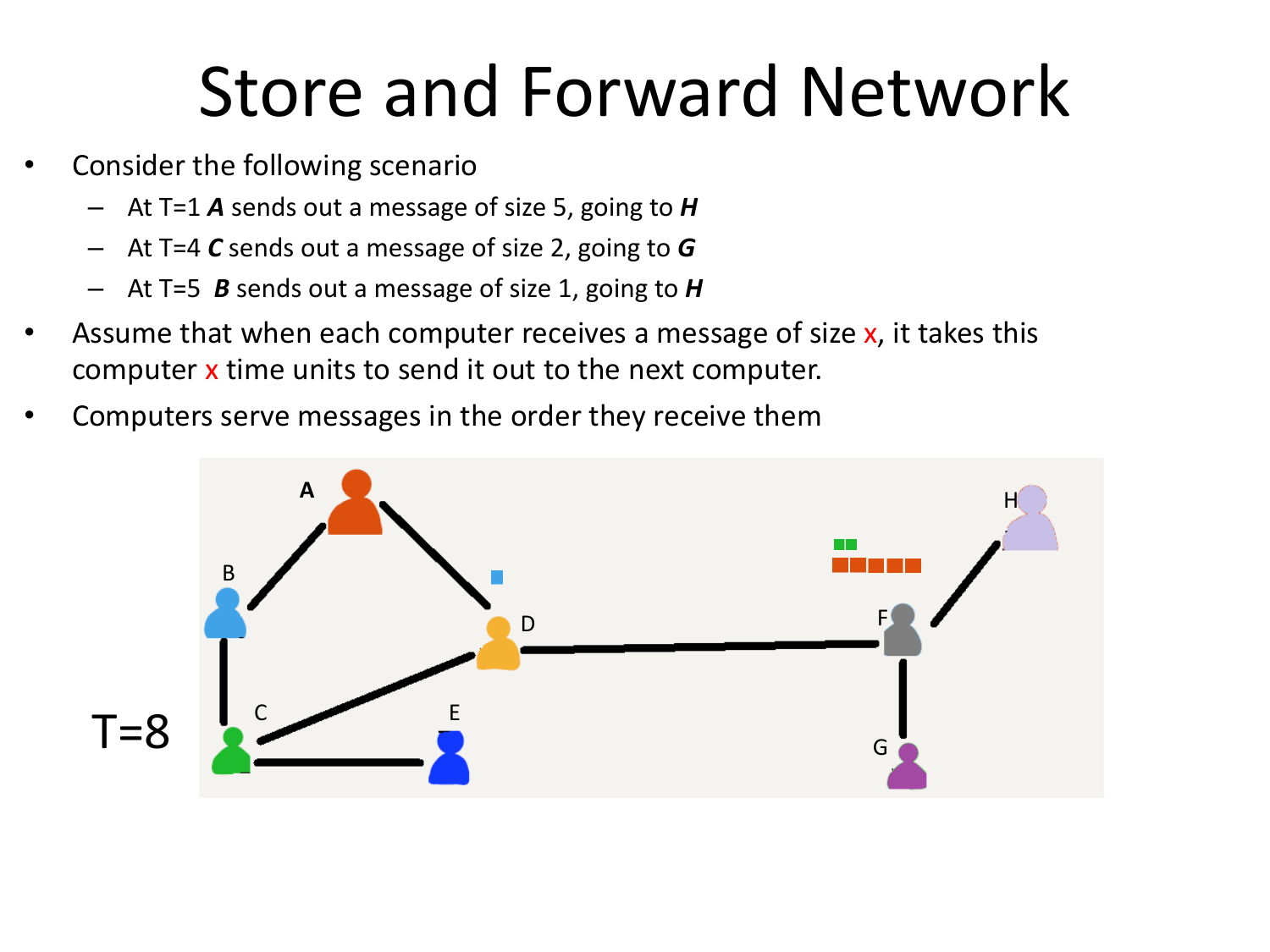
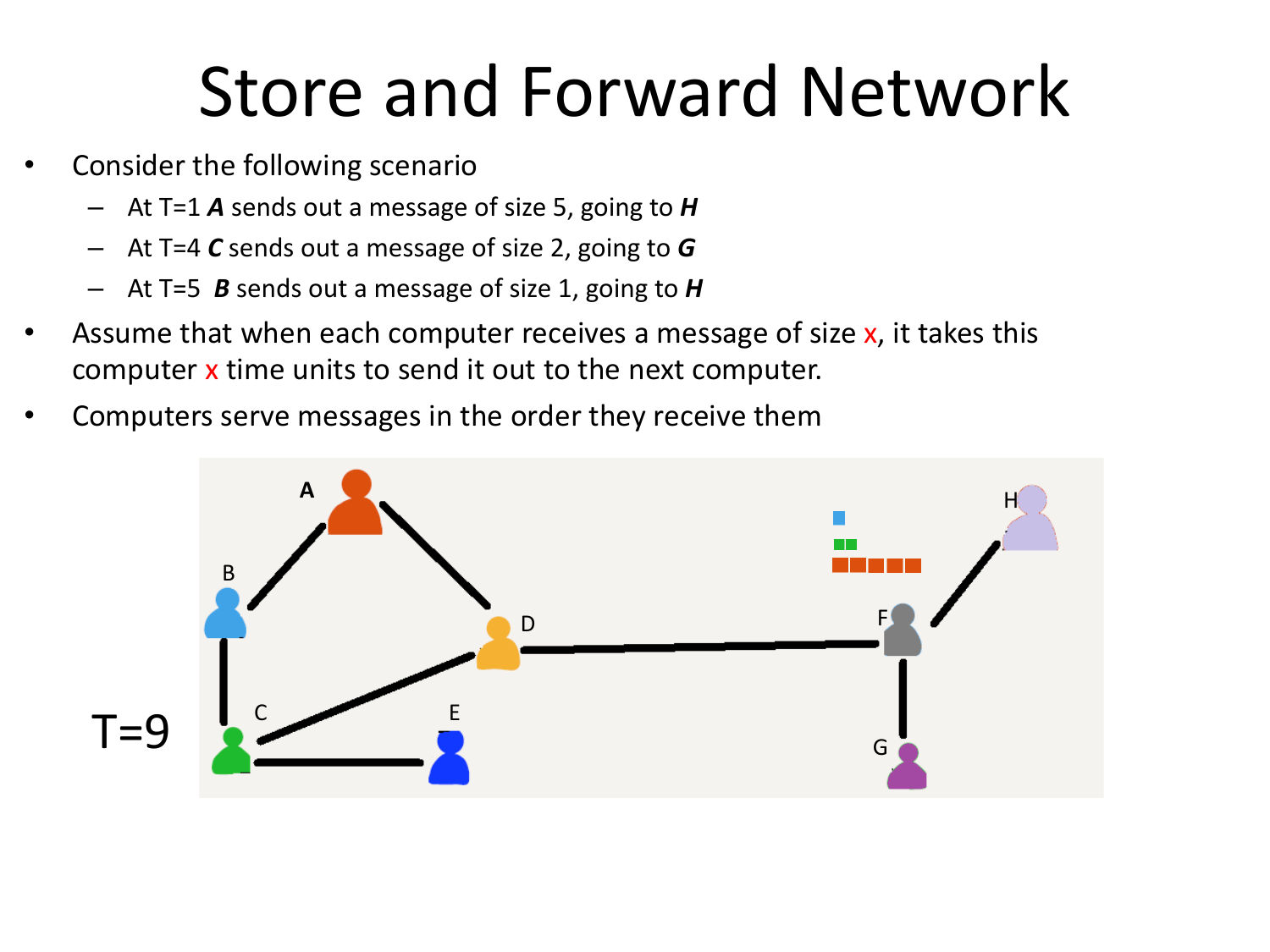
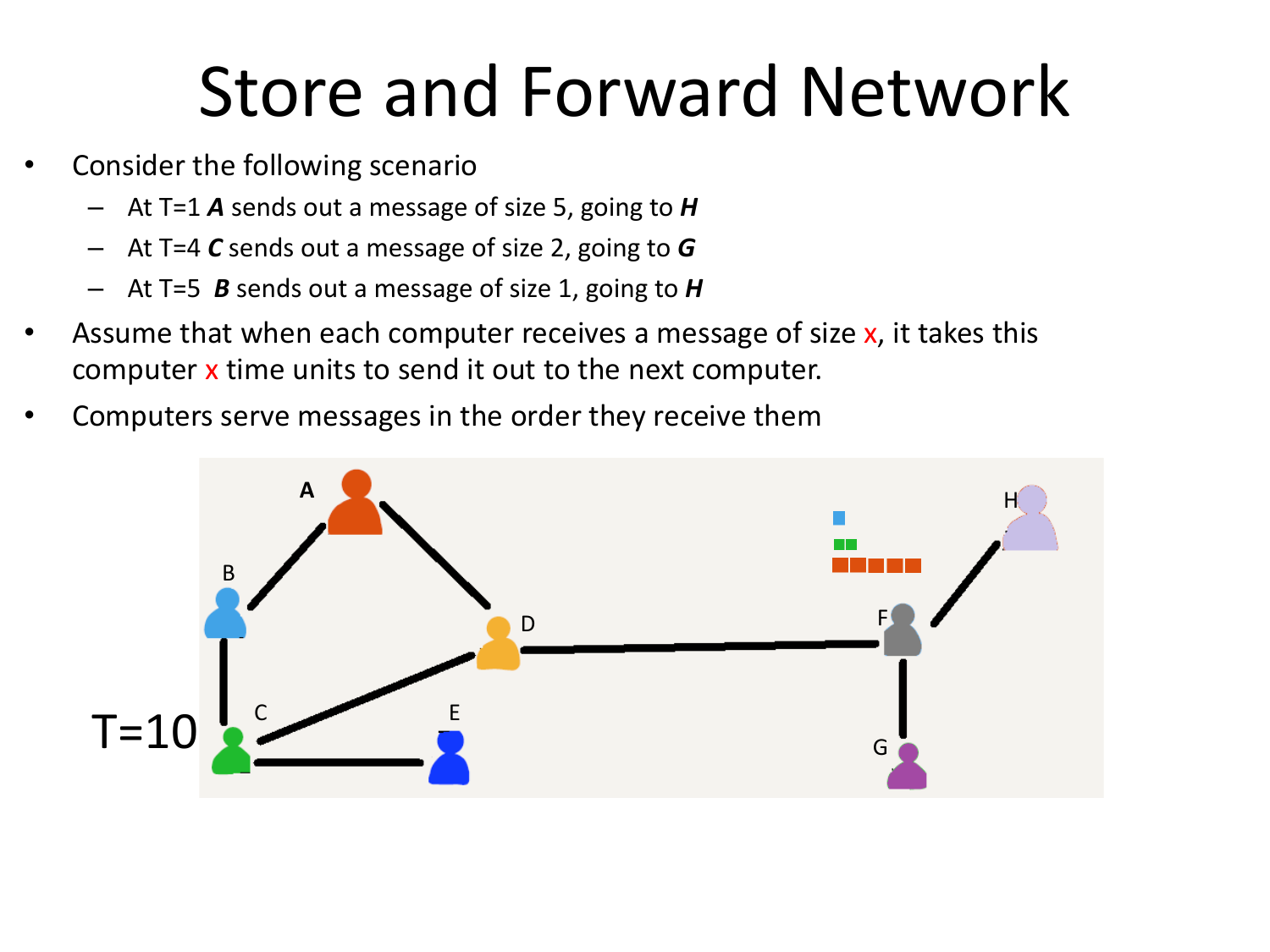
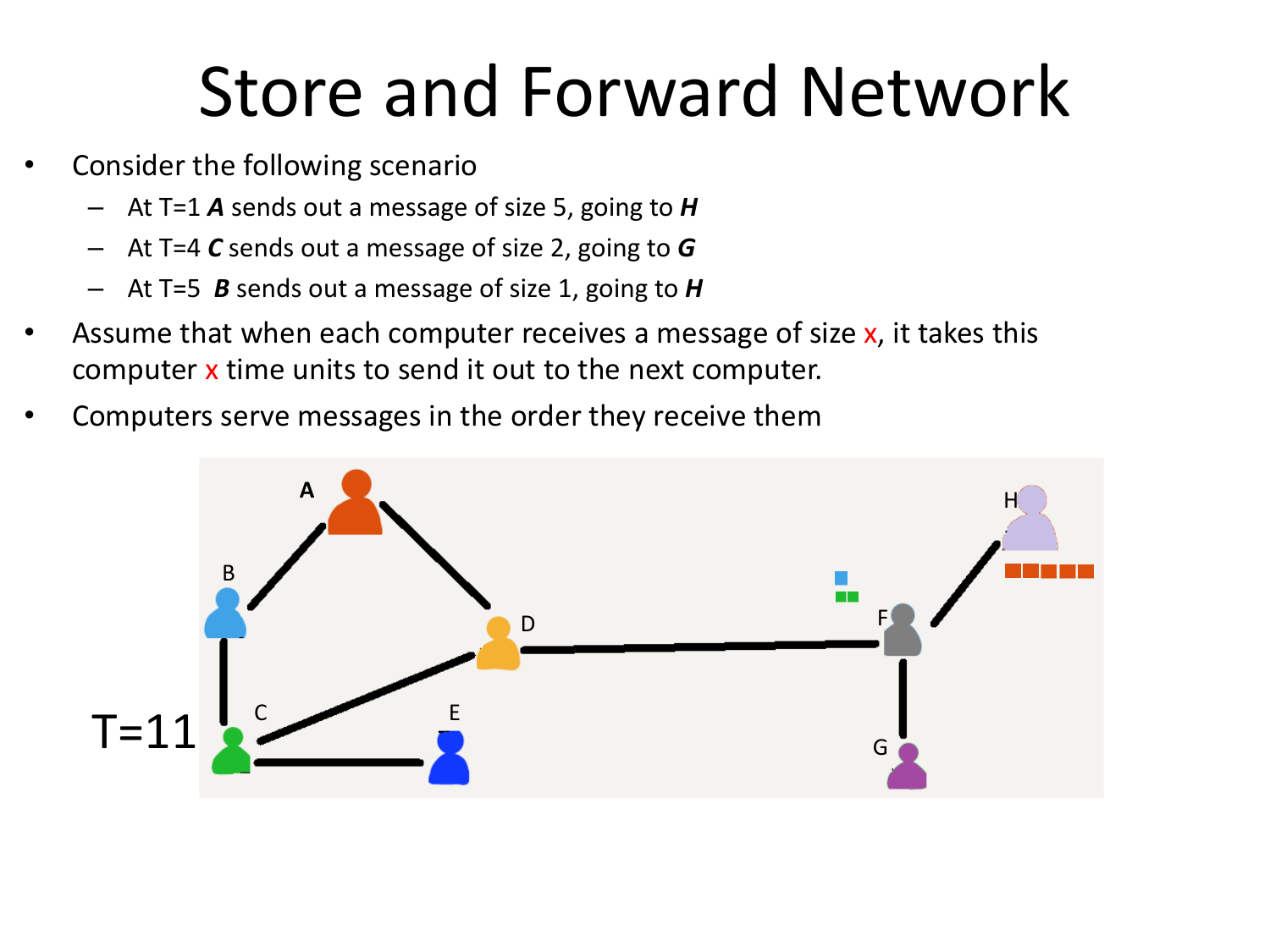
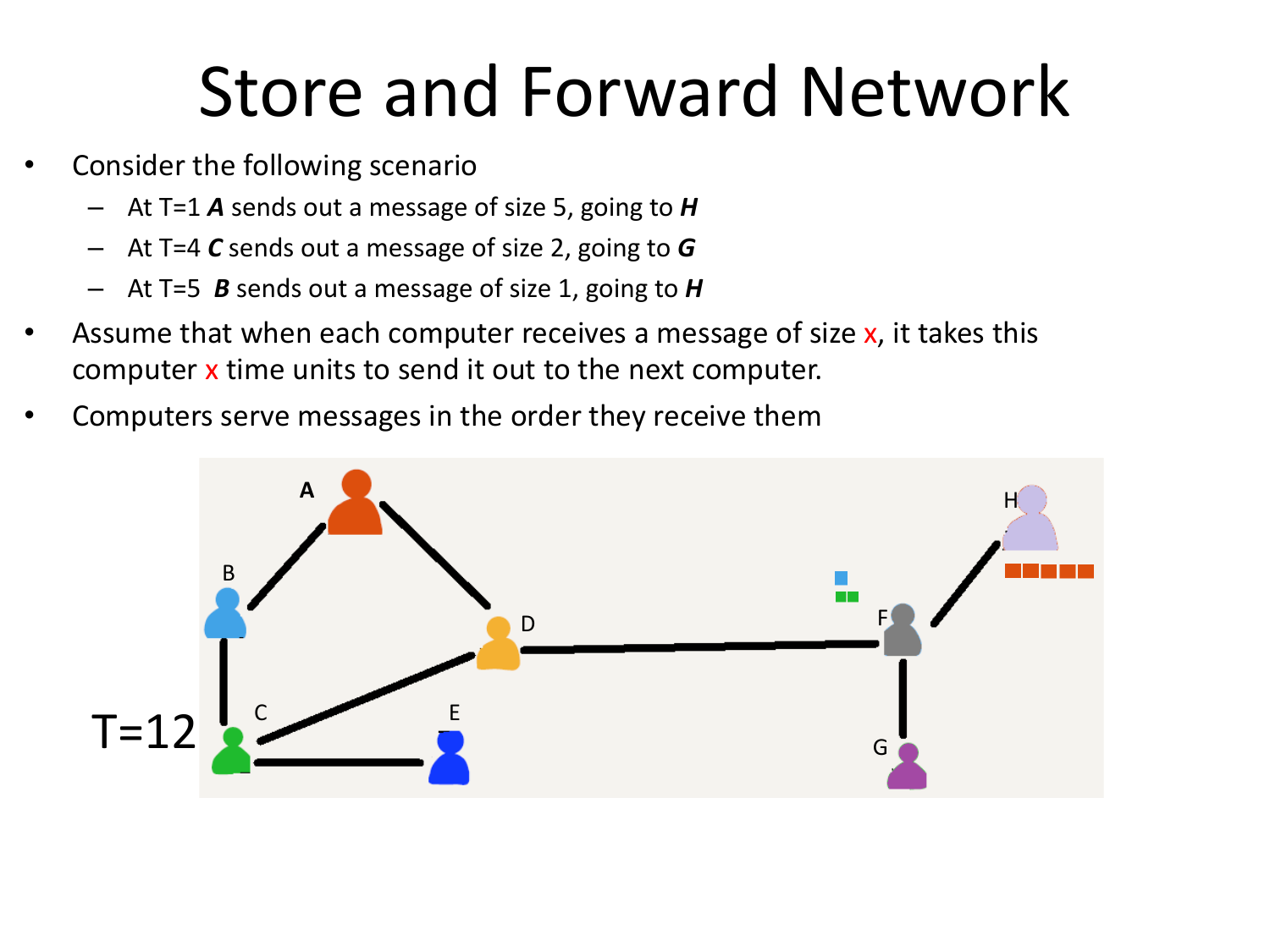
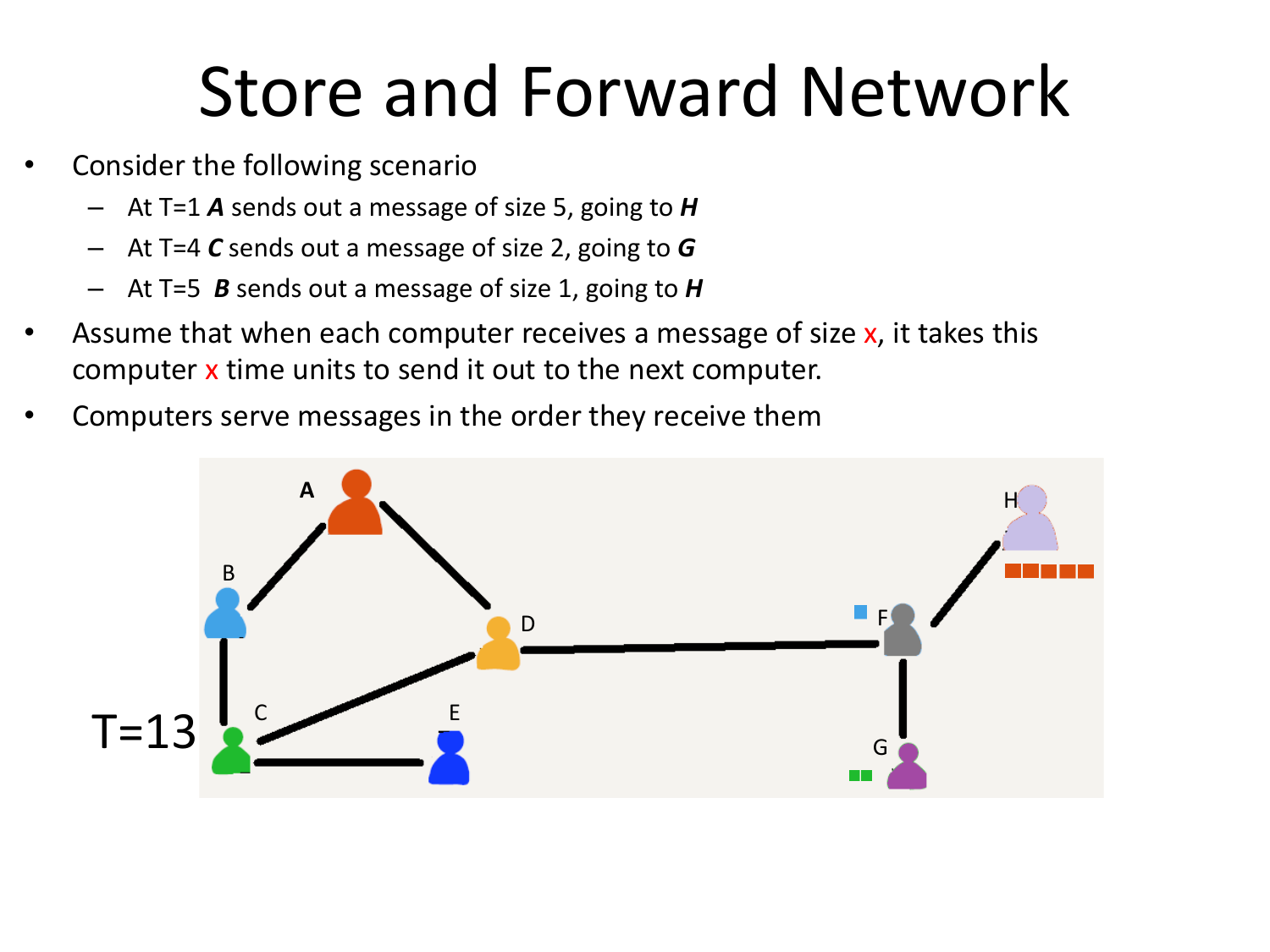
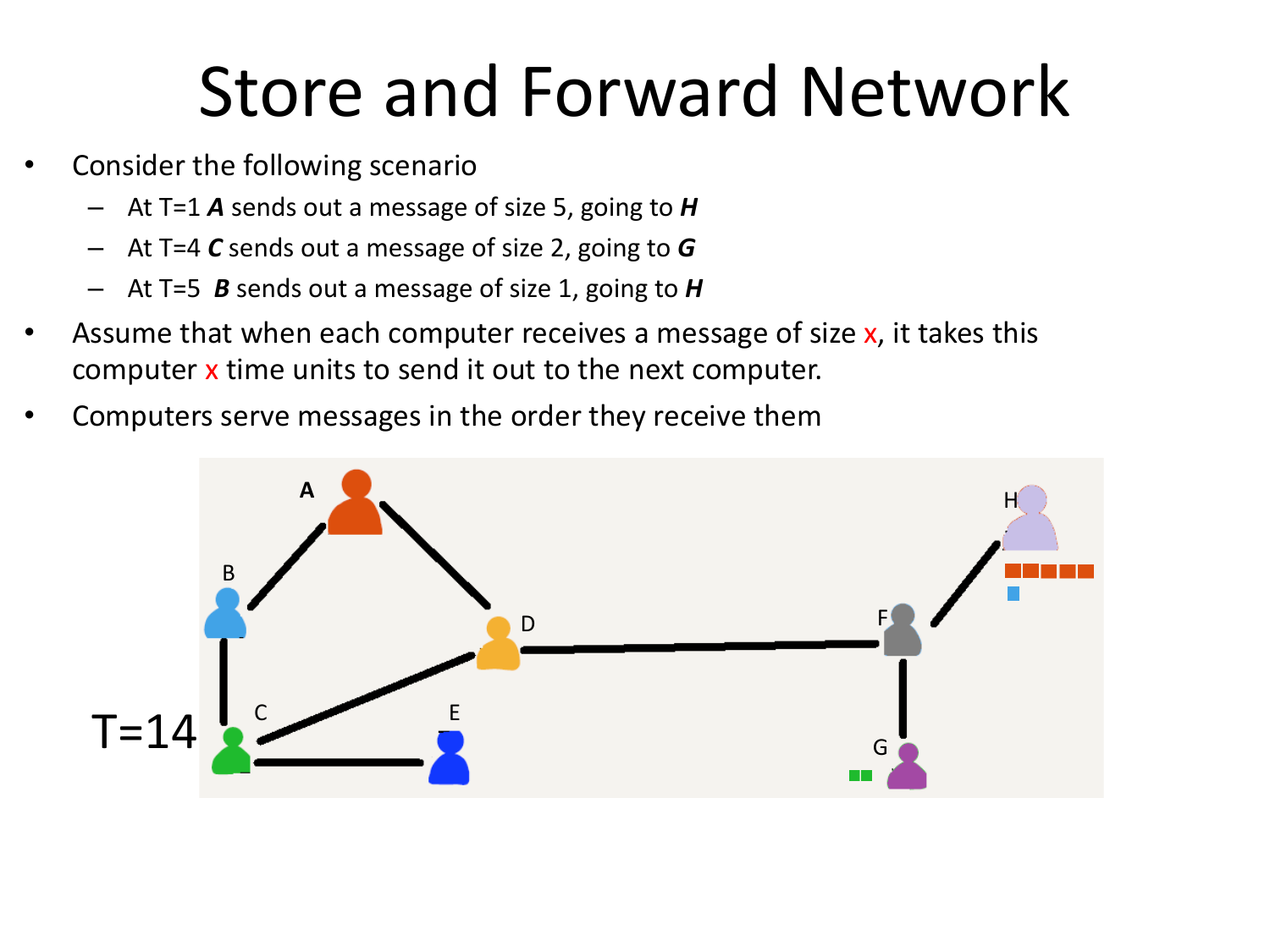

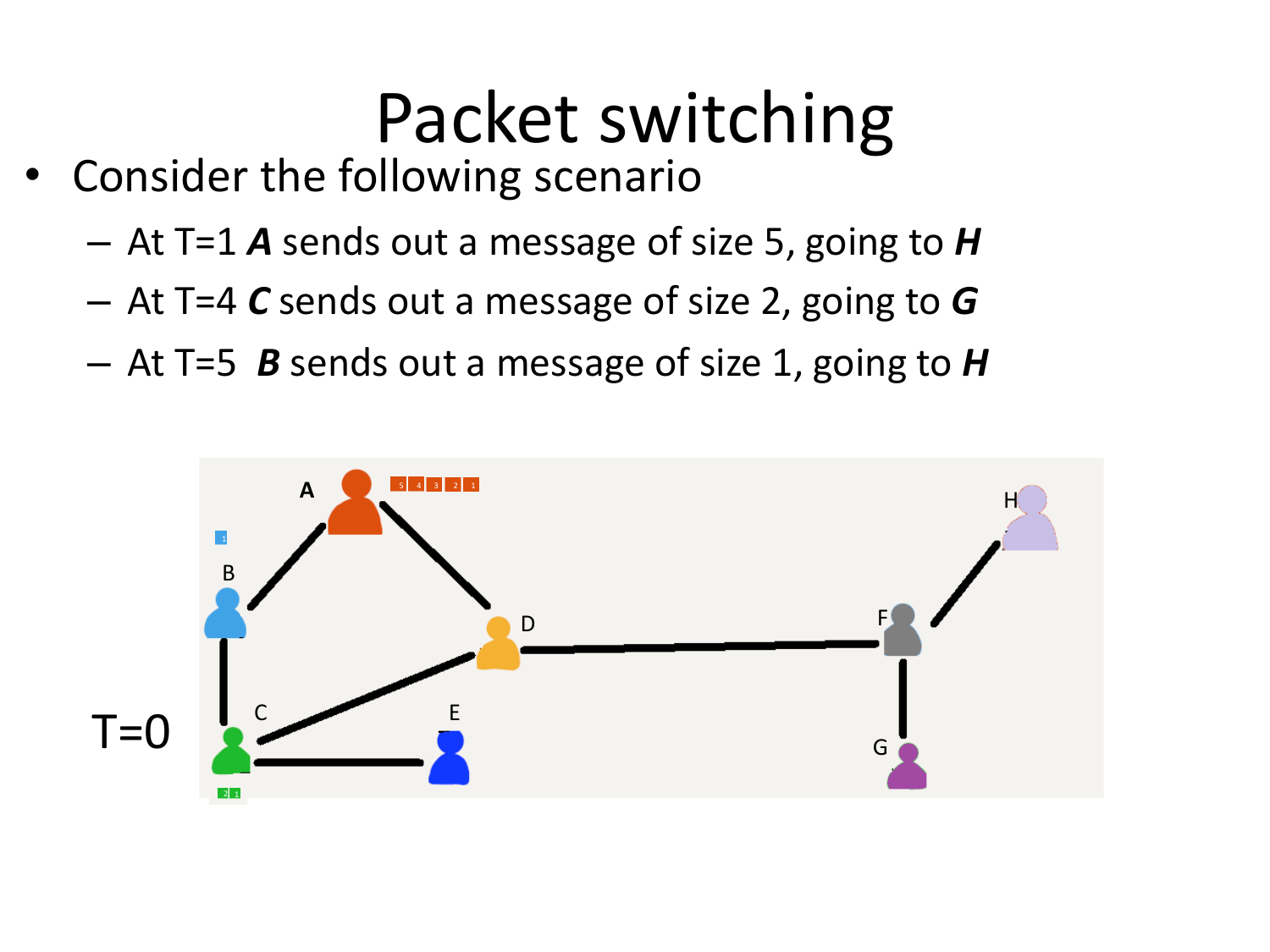
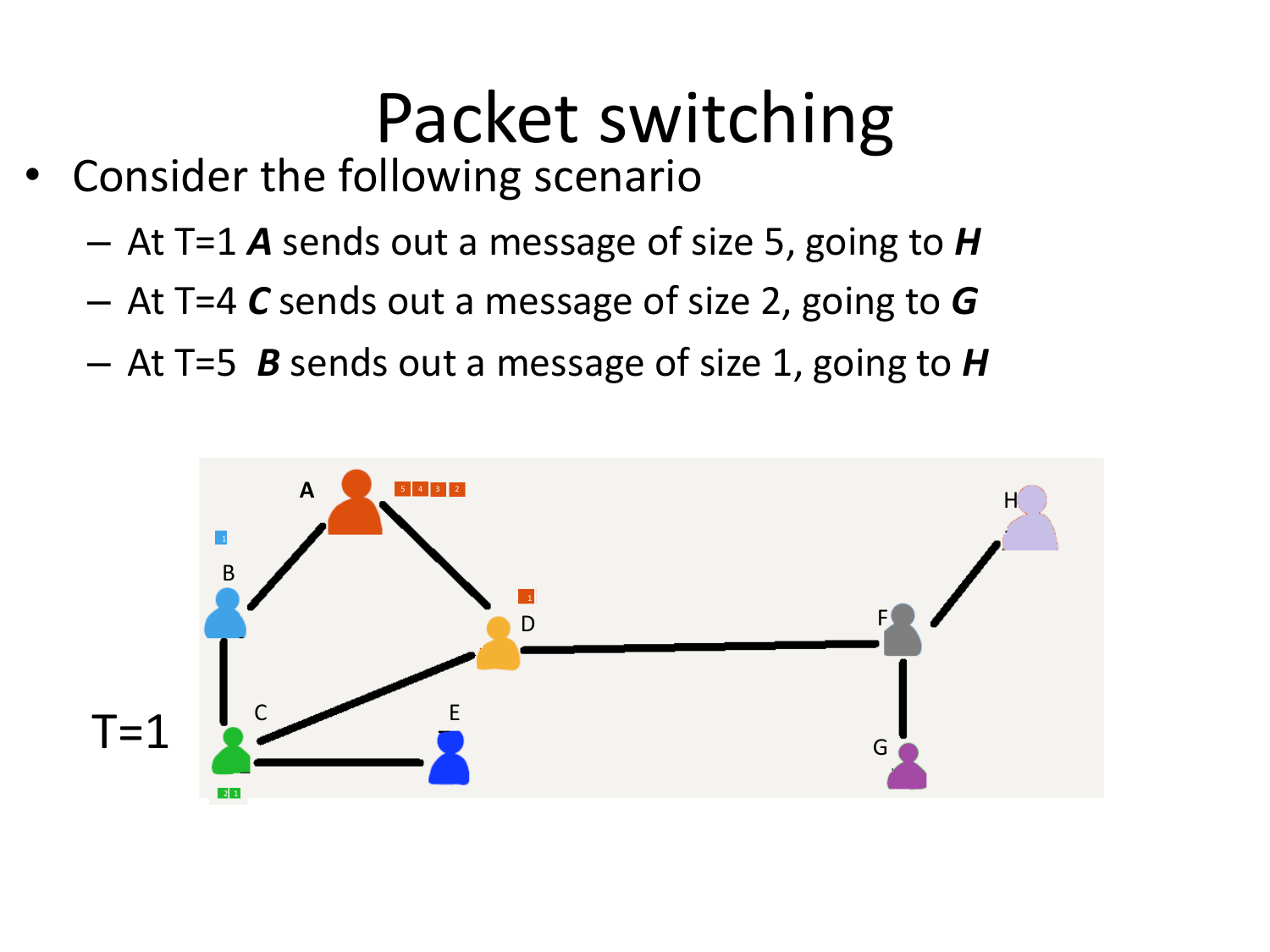
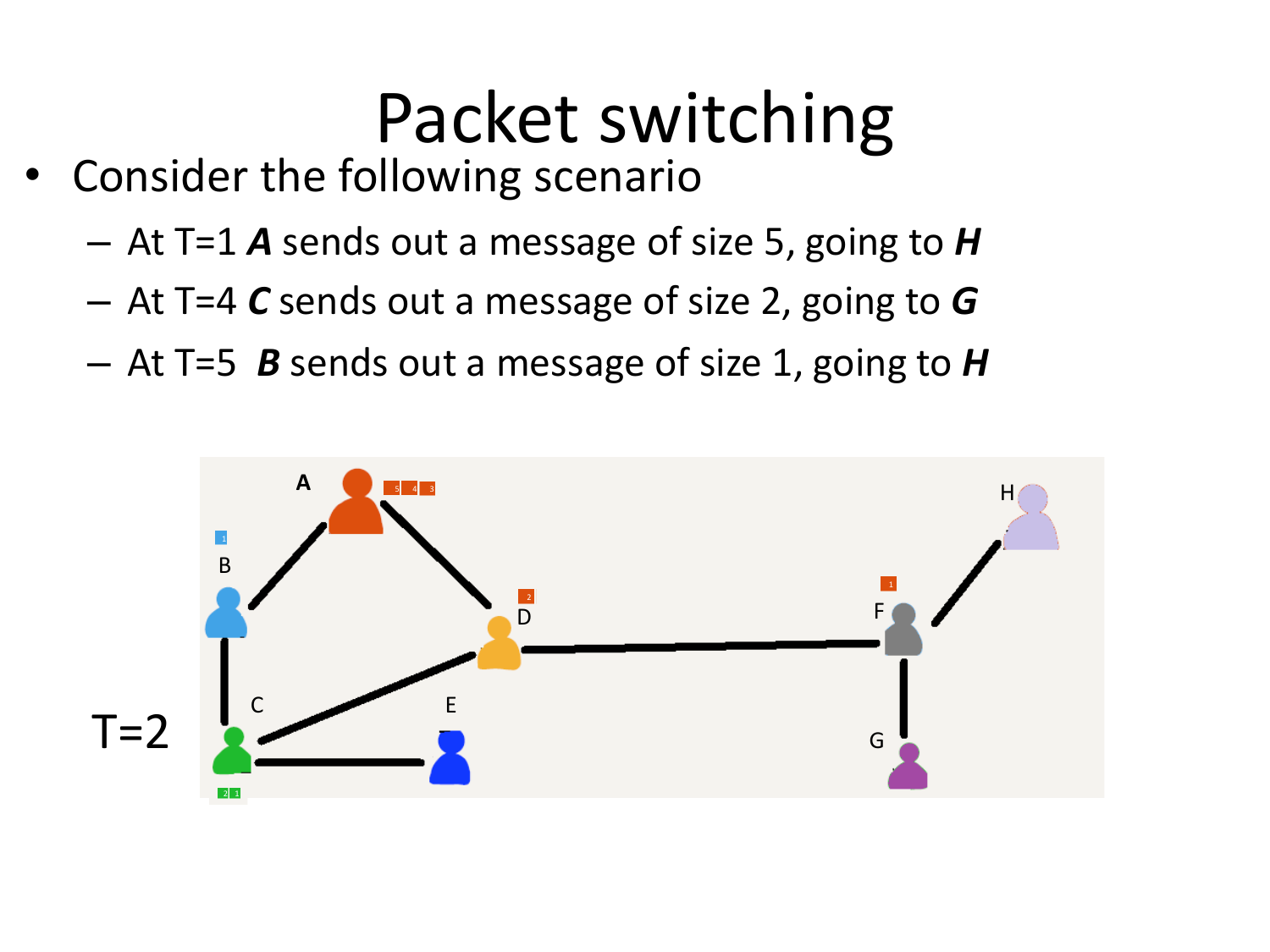
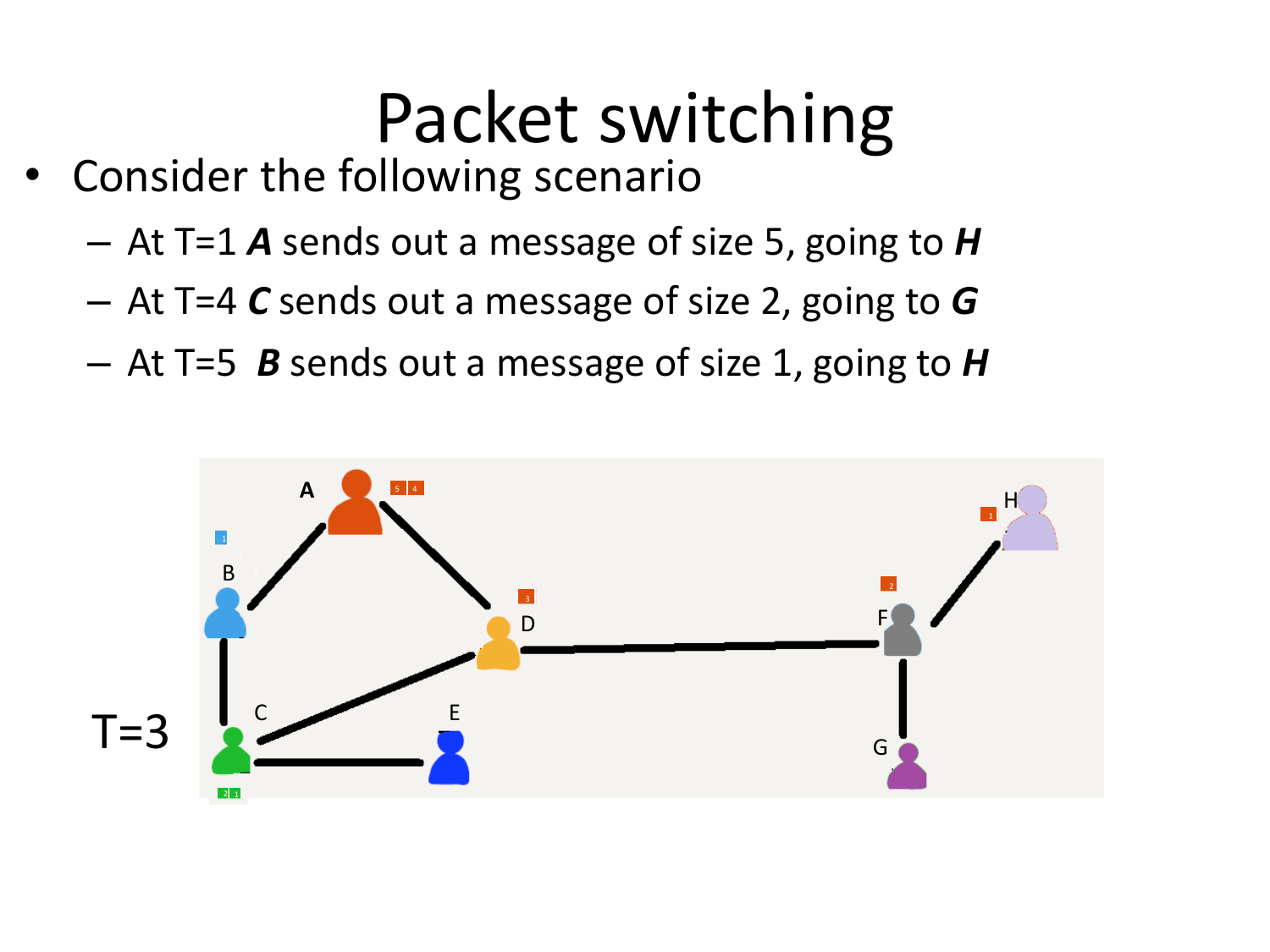
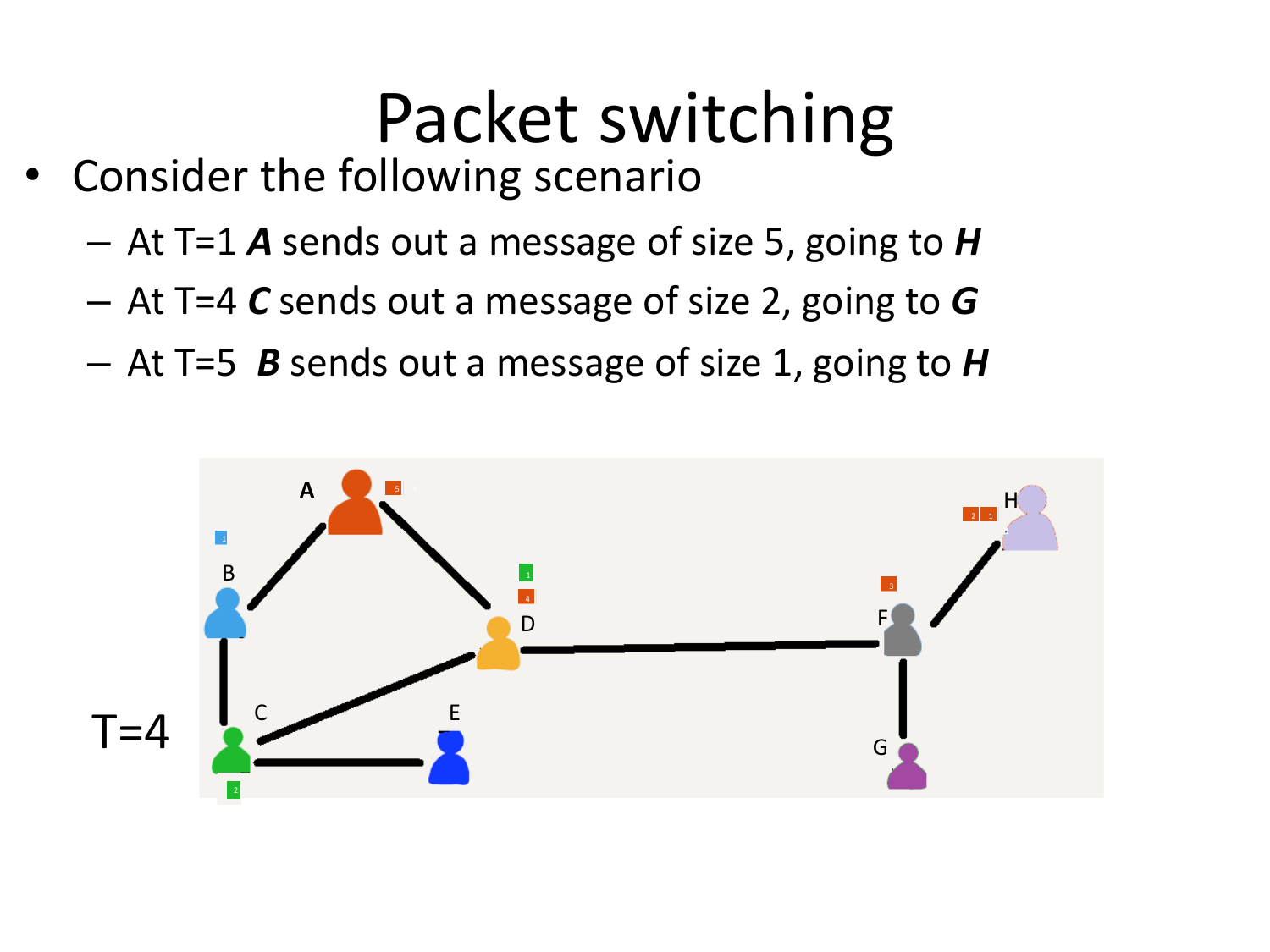
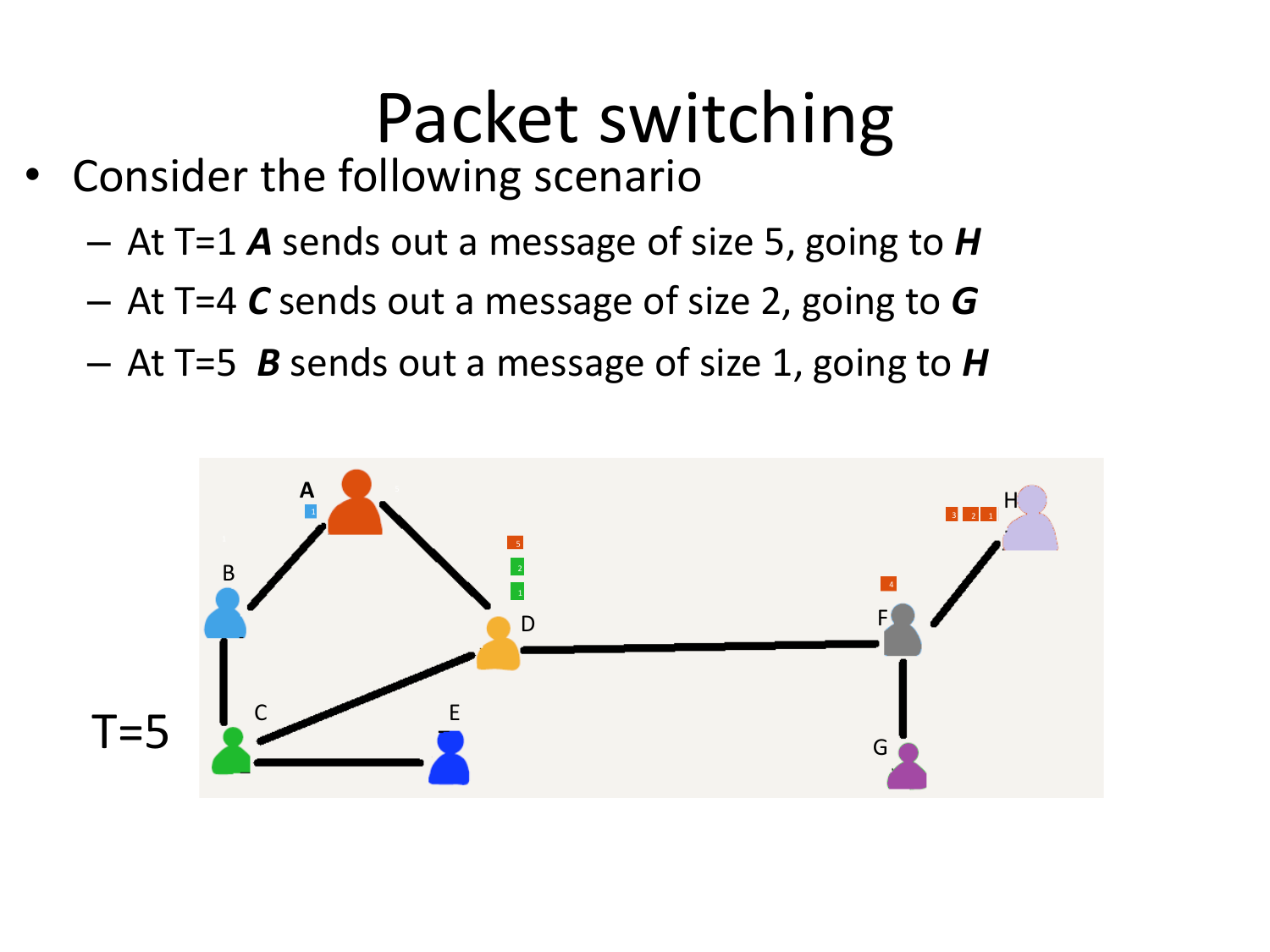
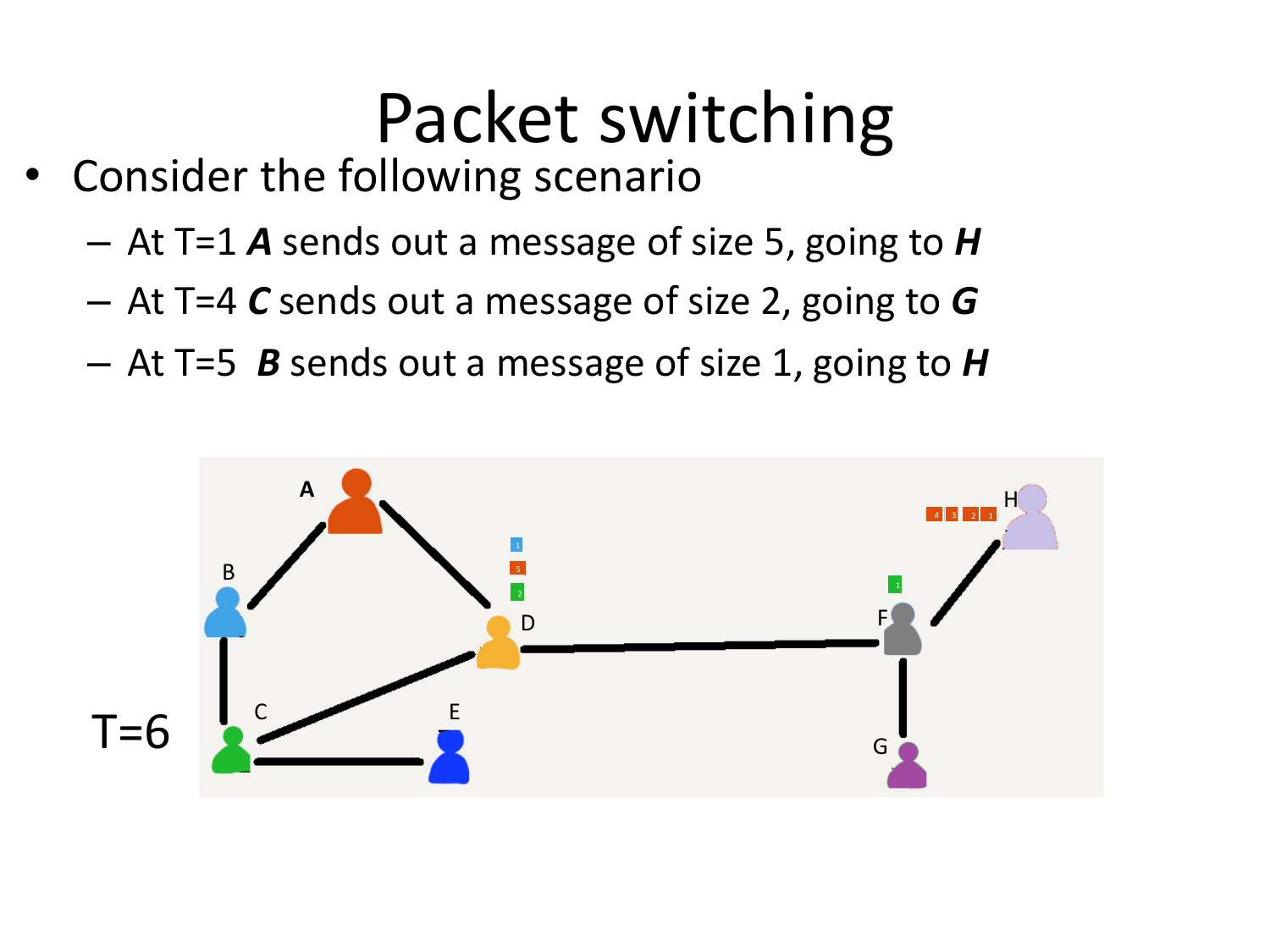
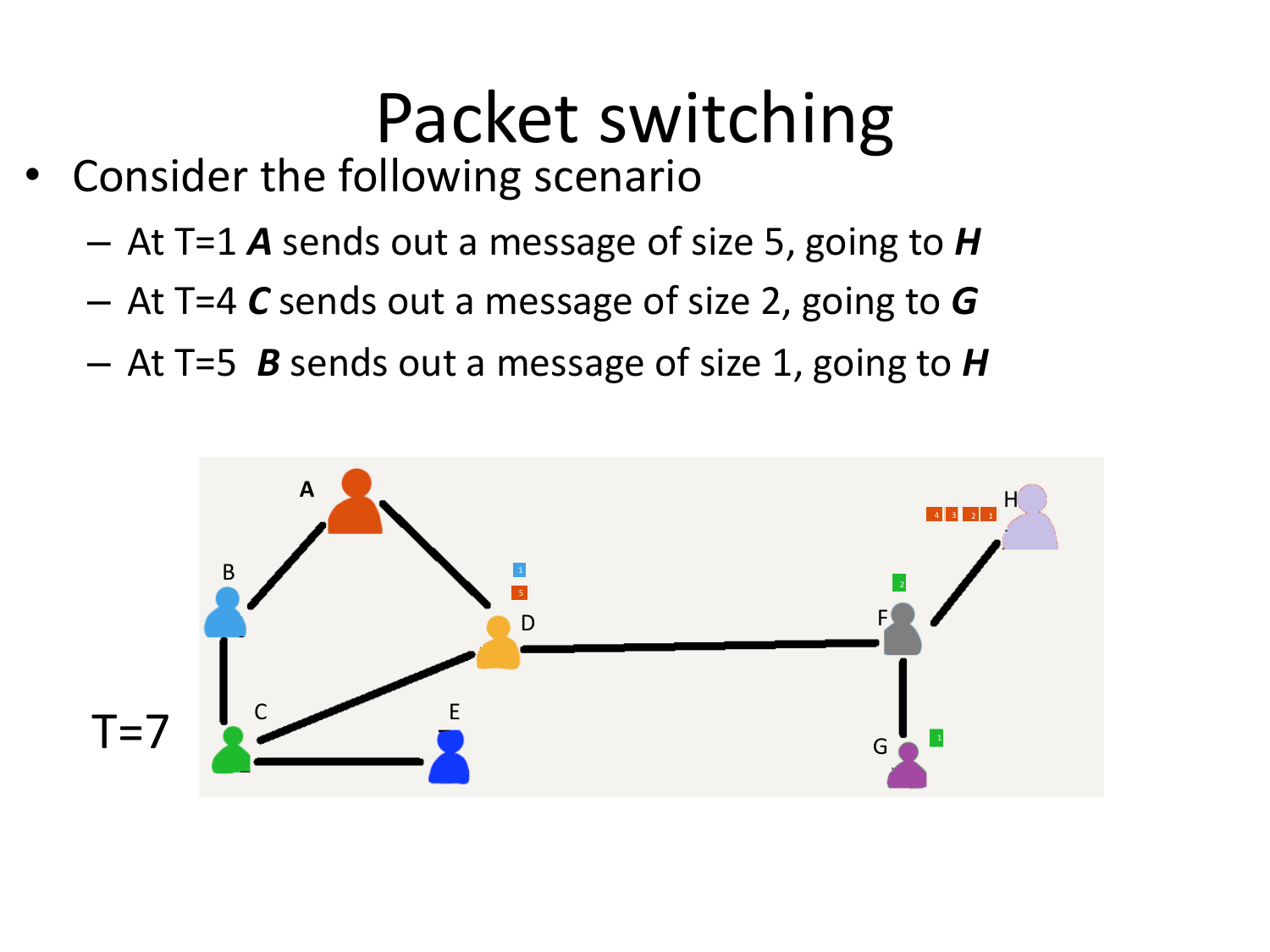
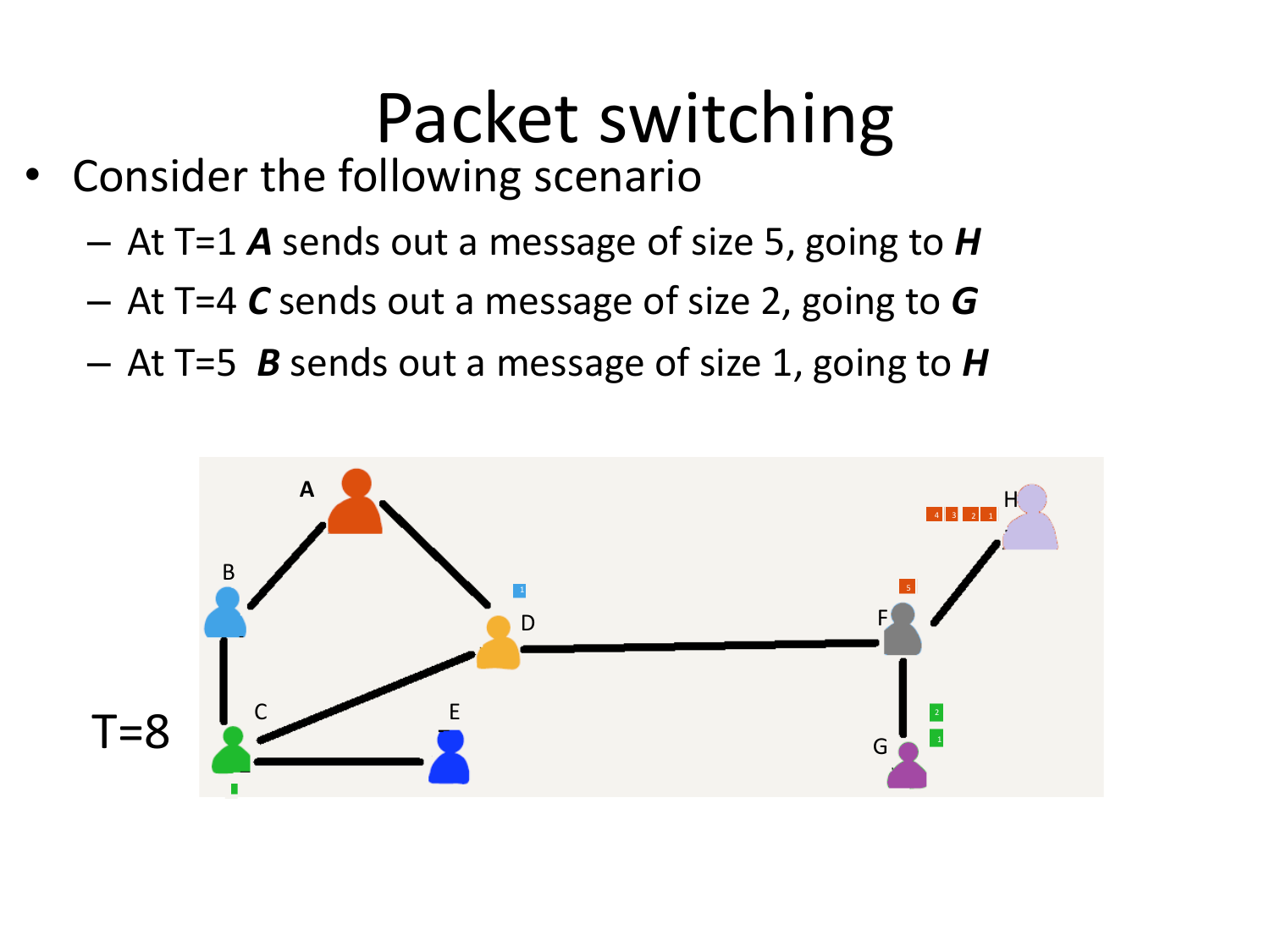
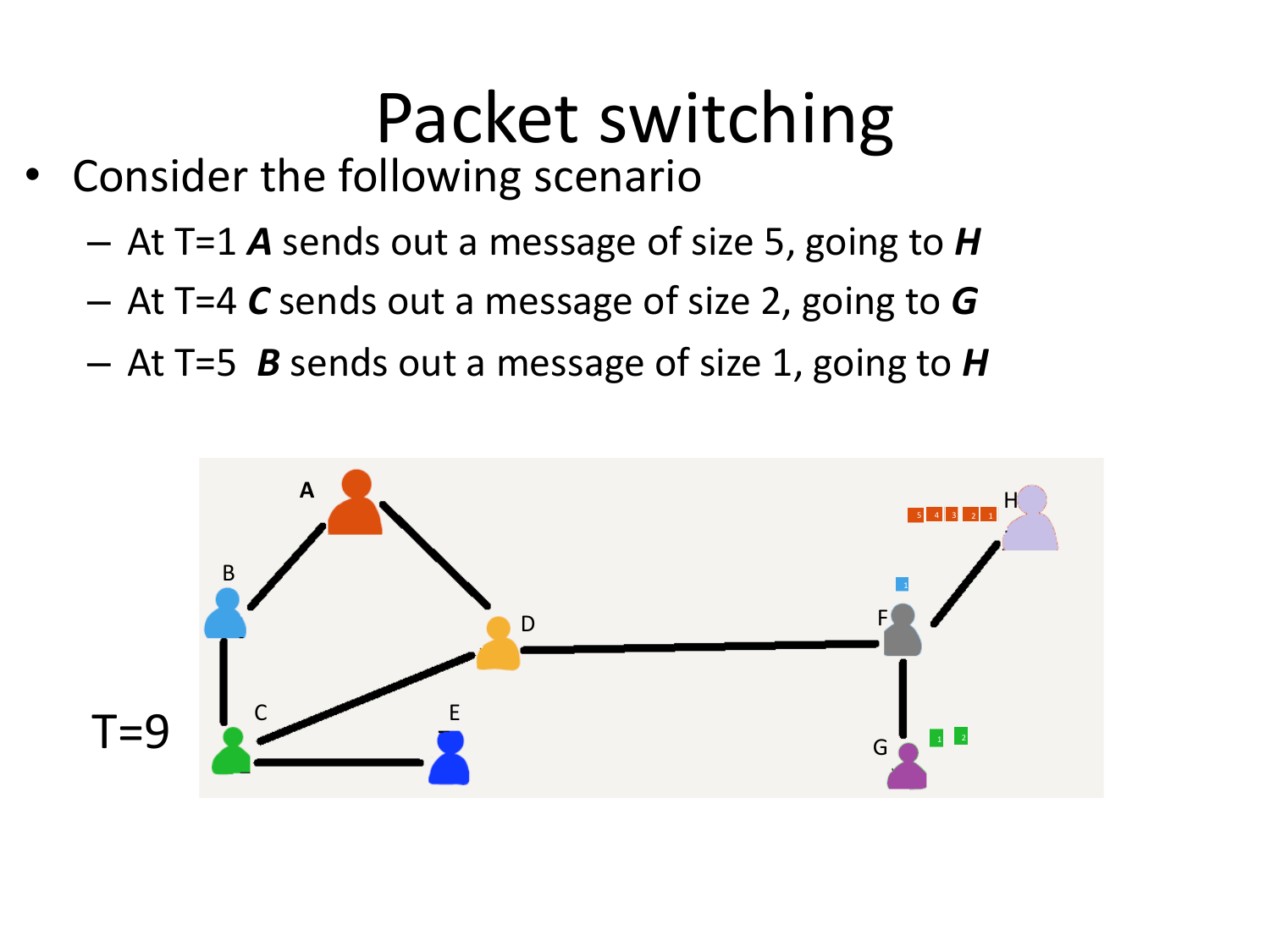
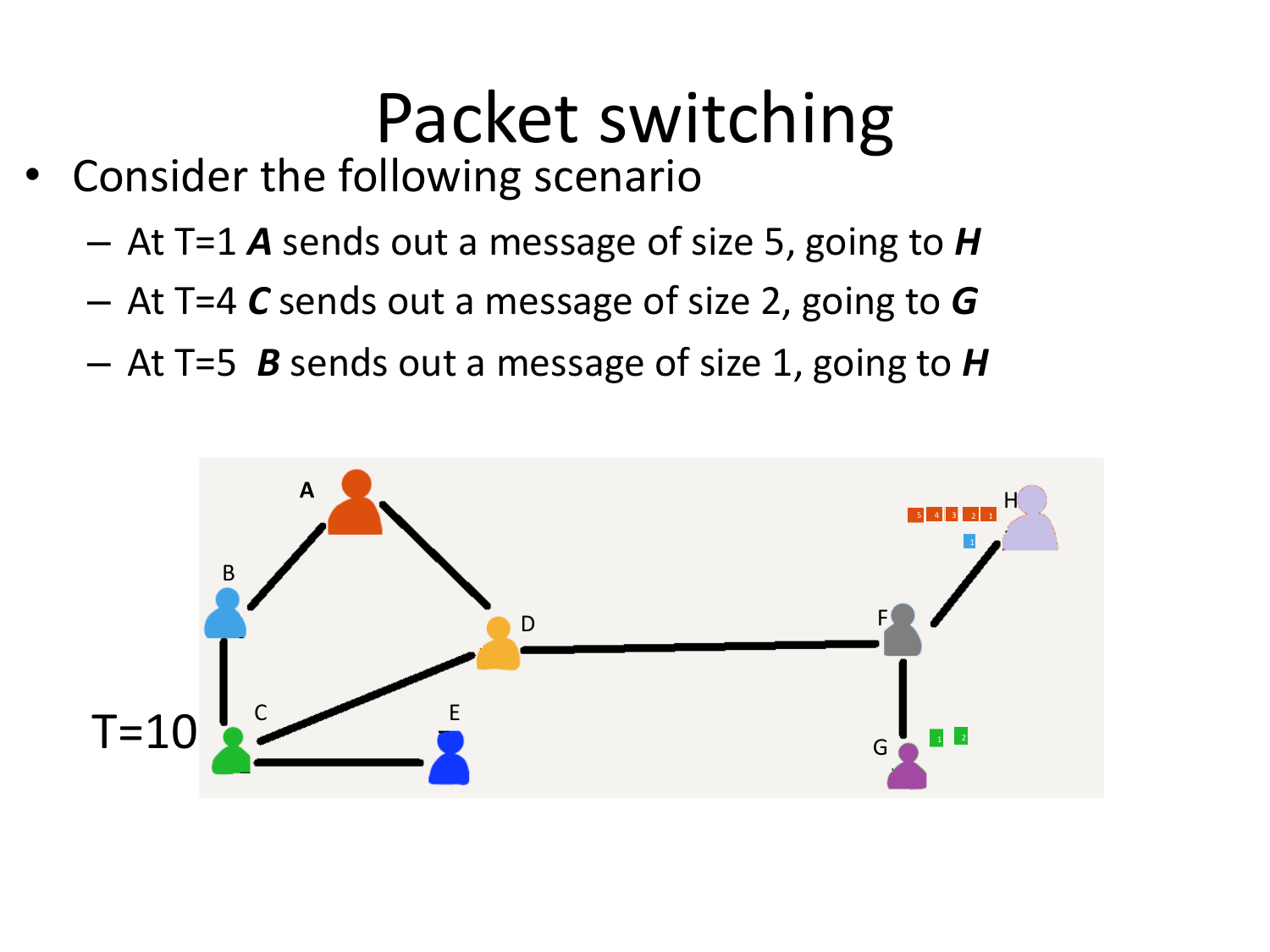
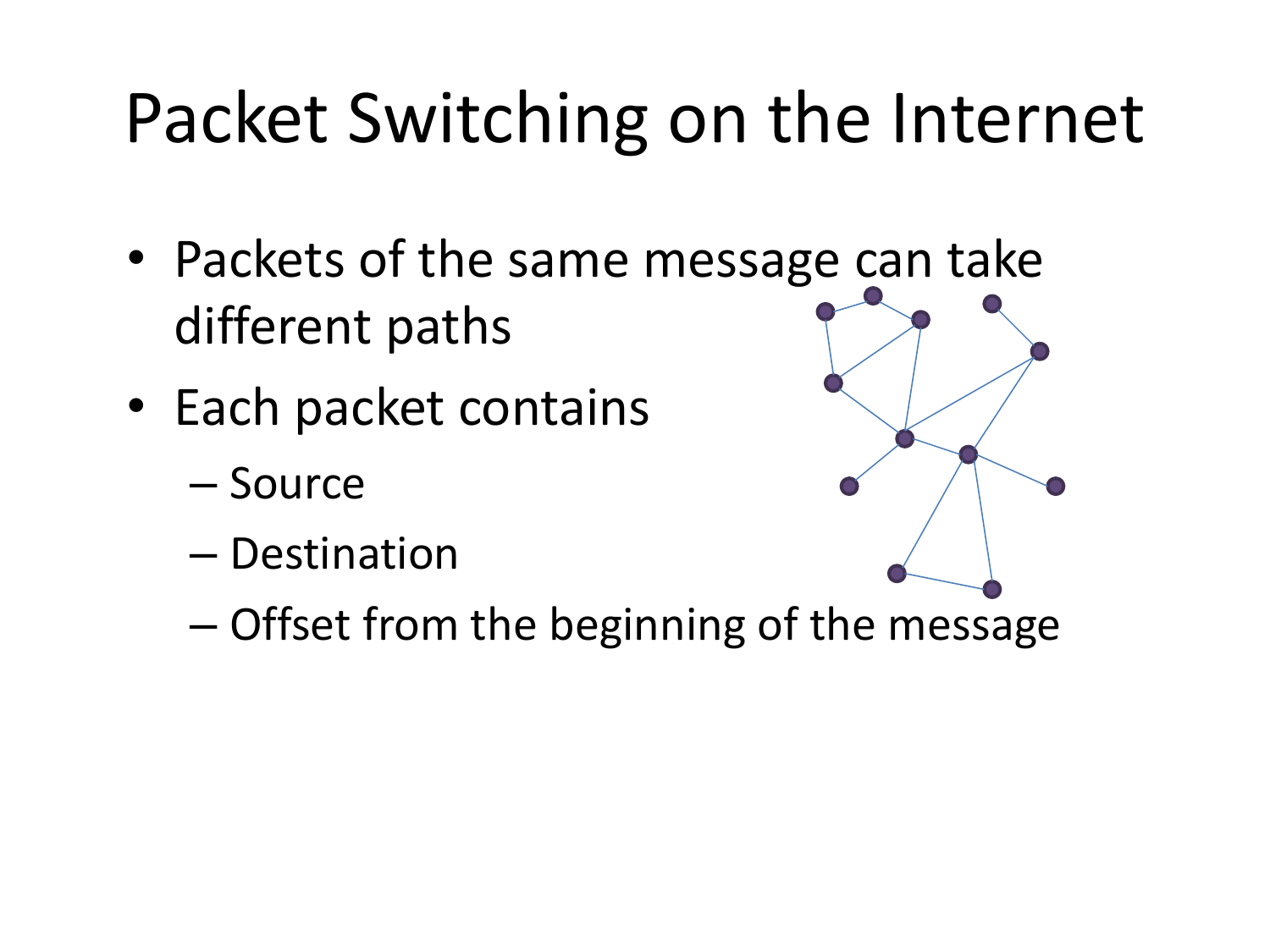
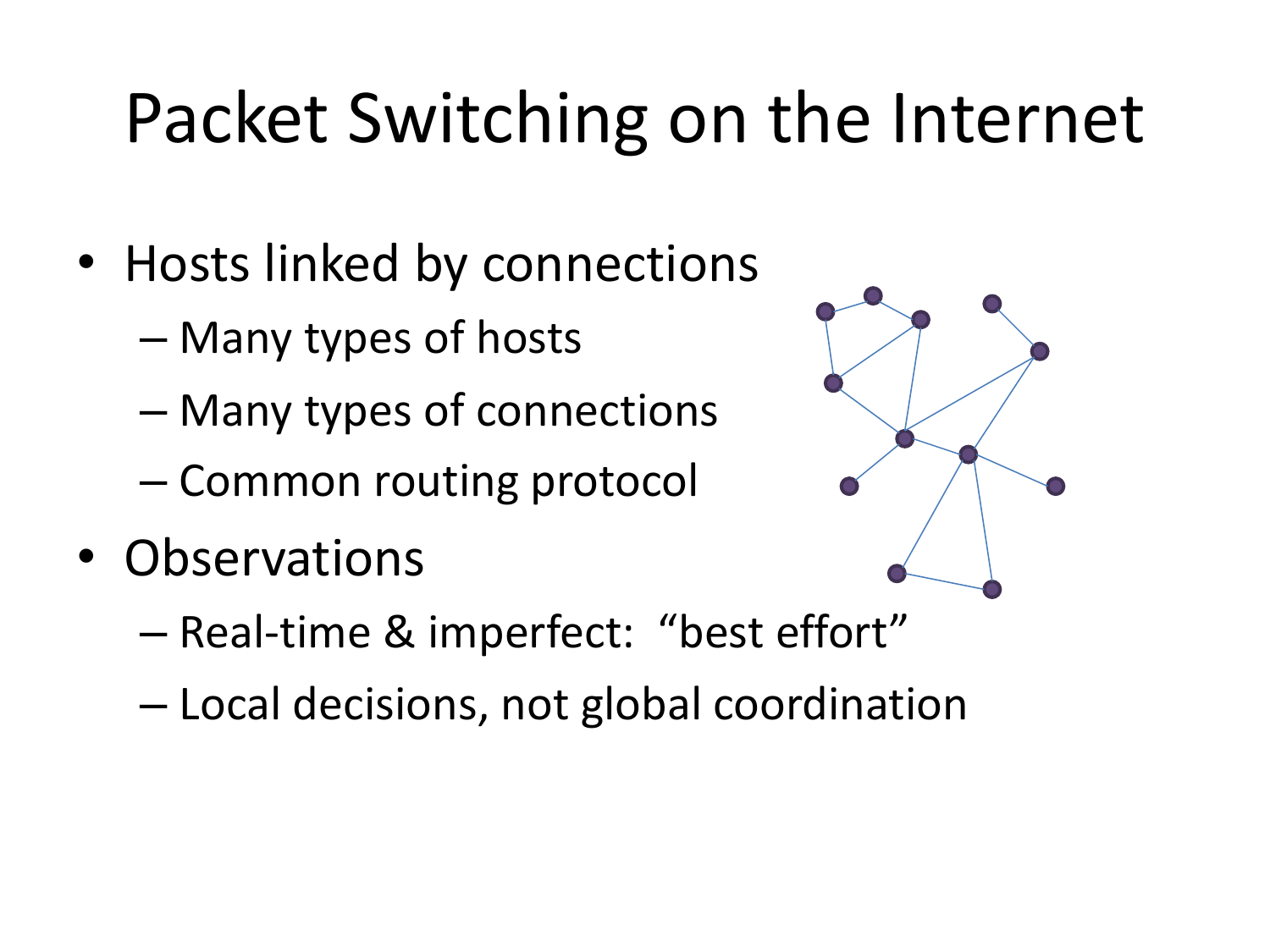
Please fill this out before leaving: